Understanding chatbots vs. AI agents in 2026 | A complete guide
Discover how AI agents go beyond chatbots to reason, act, and automate real workflows. Learn key differences, benefits, and what’s coming by 2026.
Chatbots have evolved significantly over the years and continue to play a crucial role in customer support. They handle FAQs, guide users through predefined workflows, and help reduce support costs. But as customer expectations rise and digital interactions become more complex, traditional chatbots often fall short — limited by scripted responses and shallow understanding.
That’s where AI agents come in. Unlike chatbots, AI agents are intelligent, context-aware systems powered by large language models (LLMs) that can reason, take action, and learn from interactions. Instead of just responding to messages, they connect to your tech stack, trigger workflows, and complete tasks autonomously—from creating support tickets and updating CRM data to processing refunds or scheduling meetings.
This evolution marks a major turning point in customer support automation and AI-driven business operations. While chatbots focus on conversation, AI agents focus on outcomes—delivering faster resolutions, higher accuracy, and better customer satisfaction.
In this article, we’ll explore:
The key differences between chatbots and AI agents
When to use each for maximum ROI
How AI agents outperform chatbots in modern support and sales environments
What to look for when choosing an AI agent platform for your business
Let’s also learn why leading companies are replacing their chatbots with intelligent AI agents — and how seeing one in action through a live demo can reveal the true impact of next-generation automation.
What are chatbots, and how do they work?
Chatbots are software applications designed to simulate human conversation through text or voice. They’re programmed to interpret user inputs, match them to predefined intents, and deliver scripted responses. The goal is to automate simple, repetitive interactions such as answering FAQs, booking appointments, or routing users to the right team.
How chatbots work
At their core, most chatbots operate on a combination of rules, decision trees, and natural language processing (NLP) to interpret queries and respond appropriately. Here’s how the workflow typically looks:
Pattern matching and keyword recognition
Traditional chatbots scan user messages for keywords or patterns that match predefined triggers. For example, if a message includes “refund” or “cancel order,” the bot routes the user to a refund workflow. This works well for predictable queries but fails when phrasing or context changes.
Intent classification systems
More advanced bots use intent classification, powered by NLP. Instead of relying solely on exact words, they analyze meaning — grouping phrases like “I need help logging in” and “can’t access my account” under the same intent. Each intent is manually trained with example phrases, so the chatbot can recognize similar user inputs in the future.
Pre-programmed response libraries
Once an intent is detected, the chatbot retrieves an answer from a pre-programmed response library or runs a predefined action, such as displaying order status. These responses are curated by admins or support teams, ensuring accuracy but limiting flexibility.
Limitations of scripted conversations
While effective for high-volume, repetitive tasks, these bots are limited in their ability to be reactive and linear. They can’t reason, learn from context, or handle multi-step processes. When conversations drift beyond training data, they often loop, stall, or escalate to humans.
What are AI agents, and how do they work
If chatbots are designed to talk, AI agents are built to think and act. They represent the next leap in conversational automation, combining language understanding, reasoning, and system-level execution.
Unlike chatbots that stop at generating responses, AI agents can perform real tasks. They connect to business systems like CRMs, ticketing tools, or HR platforms, enabling actions such as creating support tickets, updating records, processing returns, or scheduling meetings, all without human intervention.
Core technologies powering AI agents
AI agents rely on a powerful mix of:
Large Language Models (LLMs) for understanding context and generating natural responses.
Tool and API integrations to execute commands within apps like Zendesk, Salesforce, or Slack.
Memory and reasoning layers that help the agent remember context, plan next steps, and adapt to user behavior over time.
How AI agents work
AI agents are designed to go beyond conversation, they understand intent, make decisions, and take action. Instead of following rigid scripts, they use reasoning, memory, and integrations to achieve outcomes autonomously.
Understanding user intent
When a user sends a message, the AI agent uses Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Large Language Models (LLMs) to interpret the meaning, tone, and context. It doesn’t just match keywords — it understands the intent behind the message.
Planning and reasoning
Once the intent is clear, the agent applies reasoning models to plan the best next steps. It can break down complex requests into smaller tasks, determine dependencies, and decide which tools or systems to use — much like how a human support rep thinks through a problem.
Taking action across systems
Here’s where AI agents truly differ from chatbots. They can connect to third-party tools and APIs (like CRMs, ticketing systems, or HR platforms) to execute real actions, such as creating tickets, checking orders, sending emails, or updating a customer record.
Learning and adapting
Each interaction teaches the agent something new. Through feedback loops and analytics, it learns which actions were successful, how users responded, and how to optimize future outcomes. This continuous learning makes AI agents smarter, faster, and more context-aware over time.
Escalating when needed
AI agents are also designed with governance and safety layers. When they encounter unfamiliar or sensitive scenarios, they can hand off the conversation to a live human agent, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and trust.
In essence, AI agents turn conversations into actions. They’re not just digital assistants, they’re autonomous workers capable of reasoning, executing, and improving continuously.
Chatbots vs AI agents: key differences
While both chatbots and AI agents enhance automation, their capabilities, intelligence, and outcomes differ significantly. Chatbots are rule-followers — they respond. AI agents are problem-solvers — they act.
Aspect | Chatbots | AI Agents |
Core capability | Follow predefined scripts and respond to simple inputs | Understand intent, reason, and execute actions autonomously |
Technology foundation | Rule-based logic and basic NLP | Large Language Models (LLMs), reasoning engines, and multi-tool integrations |
Context handling | Limited to current conversation | Retains context, memory, and user history for continuity |
Integration depth | Basic API or form-based workflows | Deep integration with CRMs, ERPs, HR, and IT systems |
Learning ability | Static — requires manual updates | Continuously learns and improves through feedback loops |
Response quality | Predictable but rigid | Dynamic, adaptive, and personalized |
Task execution | Responds or redirects users | Plans, executes, and completes multi-step workflows |
Human dependency | Needs human escalation for complex issues | Operates independently, escalating only when necessary |
ROI impact | Improves efficiency for FAQs and routing | Drives measurable outcomes in revenue, productivity, and satisfaction |
In short, chatbots converse, while AI agents take action. Where chatbots enhance interaction, AI agents enable execution, making them the natural evolution of conversational automation.
Types of chatbots
Not all chatbots are built the same. Their capabilities depend on how they’re designed and the level of intelligence behind them.
Rule-based chatbots
These bots follow predefined scripts or decision trees, which are ideal for answering FAQs or handling simple, repetitive queries.
A restaurant chatbot that guides users through table reservations using “yes/no” or numbered menu options.
AI-powered chatbots
Powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning, these bots understand intent and context, enabling more natural and flexible conversations.
A banking chatbot that recognizes “I lost my card” and automatically initiates the card-blocking process.
Hybrid chatbots
A blend of rule-based logic and AI intelligence. They handle routine questions with scripted flows but switch to NLP-based understanding for more complex queries.
An e-commerce chatbot that helps track orders via rules but uses AI to handle product recommendations or returns.
Types of AI agents
AI agents come in different forms, depending on how much autonomy and intelligence they’re designed to have.
Reactive agents
These agents operate based on current inputs without storing past information. They respond quickly but lack memory or long-term learning.
A customer support AI agent that instantly fetches refund status when asked but doesn’t retain prior chat history.
Limited-memory agents
They can remember recent interactions and use that context to make smarter decisions. Most modern business AI agents fall into this category.
A retail AI agent that recalls a user’s previous purchases to recommend complementary products.
Learning or adaptive agents
These agents continuously learn from user interactions and data feedback loops, improving performance and accuracy over time.
A SaaS onboarding AI agent that studies user behavior to personalize setup guidance and automate recurring tasks.
Autonomous agents
The most advanced form, capable of independent decision-making, reasoning, and task execution across multiple systems.
An enterprise AI agent that diagnoses IT issues, triggers workflows in ServiceNow, and updates the team in Slack, all without human input.
Real-world chatbot examples
Chatbots are widely used across industries to automate everyday interactions, enhance customer experiences, and reduce operational load. Here are some popular functions and the brands using them effectively.
Shopping and product recommendations
Retail brands like H&M use chatbots in their mobile apps to help customers browse collections, find the right size, and get personalized style tips — all without needing a human stylist.
Banking and customer support
Financial institutions such as Bank of America rely on chatbots like Erica to handle account inquiries, payment reminders, and spending insights. This allows customers to resolve issues instantly through conversational banking.
IT helpdesk and troubleshooting
Enterprise teams deploy AI-powered chatbots like IBM Watson Assistant to automate IT support tasks such as password resets, VPN issues, and access requests — cutting ticket resolution time dramatically.
Lead qualification and sales engagement
Platforms like Drift utilize chatbots on business websites to qualify leads, capture visitor intent, and route prospects to the right sales representatives in real-time — turning website traffic into sales opportunities.
Real-world AI agent examples
AI agents are redefining automation by going beyond scripted conversations — they reason, act, and complete real tasks across systems. Here are a few powerful examples from leading industries.
Customer support automation
Companies like Airbnb and Uber use AI agents to automatically classify, route, and resolve support tickets. These agents pull data from internal systems, update records, and even close cases without human intervention — reducing response times and improving CSAT scores.
E-commerce order management
Retail leaders such as Shopify and Amazon leverage AI agents to manage complex workflows like returns, exchanges, and order tracking. The agents sync across inventory, logistics, and CRM systems to deliver real-time updates and personalized resolutions.
IT operations and monitoring
Tech enterprises like Microsoft and ServiceNow deploy AI agents that monitor system health, detect anomalies, and trigger automated fixes — ensuring uptime and minimizing manual troubleshooting.
Sales and lead management
B2B companies like HubSpot and Salesforce use AI agents to qualify leads, update CRM data, schedule follow-ups, and personalize outreach — freeing sales reps to focus on high-intent opportunities.
HR and employee self-service
Global enterprises such as Unilever and Accenture use AI agents to assist employees with HR queries, automate onboarding workflows, and handle policy or benefits requests — reducing HR workload and improving internal efficiency.
Finance and accounting automation
Organizations like JPMorgan Chase and Deloitte utilize AI agents for financial reconciliation, anomaly detection, and compliance checks — helping finance teams operate faster and more accurately.
Similarities between chatbots and AI agents
Although chatbots and AI agents differ in intelligence and complexity, they share several foundational similarities — both aim to improve user experience, streamline operations, and automate communication at scale.
Automate conversations
At their core, both systems are designed to simulate human-like conversations, helping users find answers or complete actions without waiting for a human representative.
Rely on natural language processing (NLP)
Whether rule-based or AI-driven, both use NLP to interpret user queries, understand phrasing, and deliver relevant responses in real time.
Enhance efficiency and availability
Chatbots and AI agents operate 24/7, providing instant responses and ensuring businesses stay available across time zones and channels.
Integrate with business systems
Even simple chatbots can connect with CRMs, websites, or ticketing tools to retrieve information — while AI agents extend that capability to perform deeper, multi-step actions.
Reduce workload on human teams
By handling repetitive questions or tasks, both technologies allow support, sales, and HR teams to focus on higher-value or complex work.
Improve customer and employee experience
Whether answering FAQs or resolving tickets, both solutions enhance engagement and response speed — key drivers of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In essence, chatbots and AI agents share the same goal: to make digital interactions faster, smarter, and more efficient. The difference lies in how deeply they can understand context and how far they can go to complete a task.
Benefits of adopting AI agents
Adopting AI agents isn’t just about upgrading your chatbot—it’s about transforming the way your business communicates, automates, and delivers results. AI agents combine intelligence with action, helping companies move from answering questions to achieving outcomes.
End-to-end automation
AI agents go beyond conversations. They perform complete workflows—creating tickets, processing refunds, updating databases, or scheduling follow-ups—without requiring human intervention.
Higher customer satisfaction
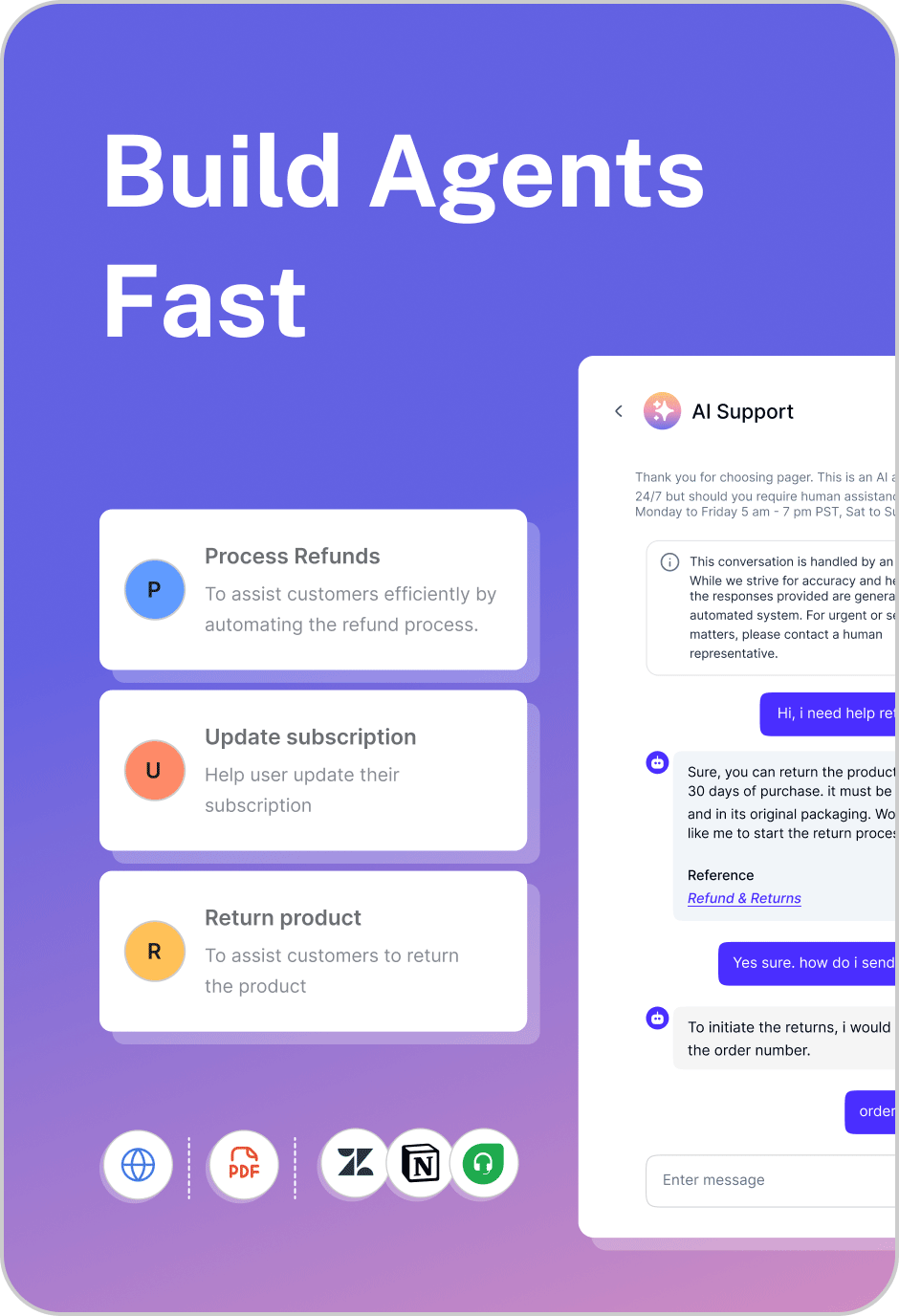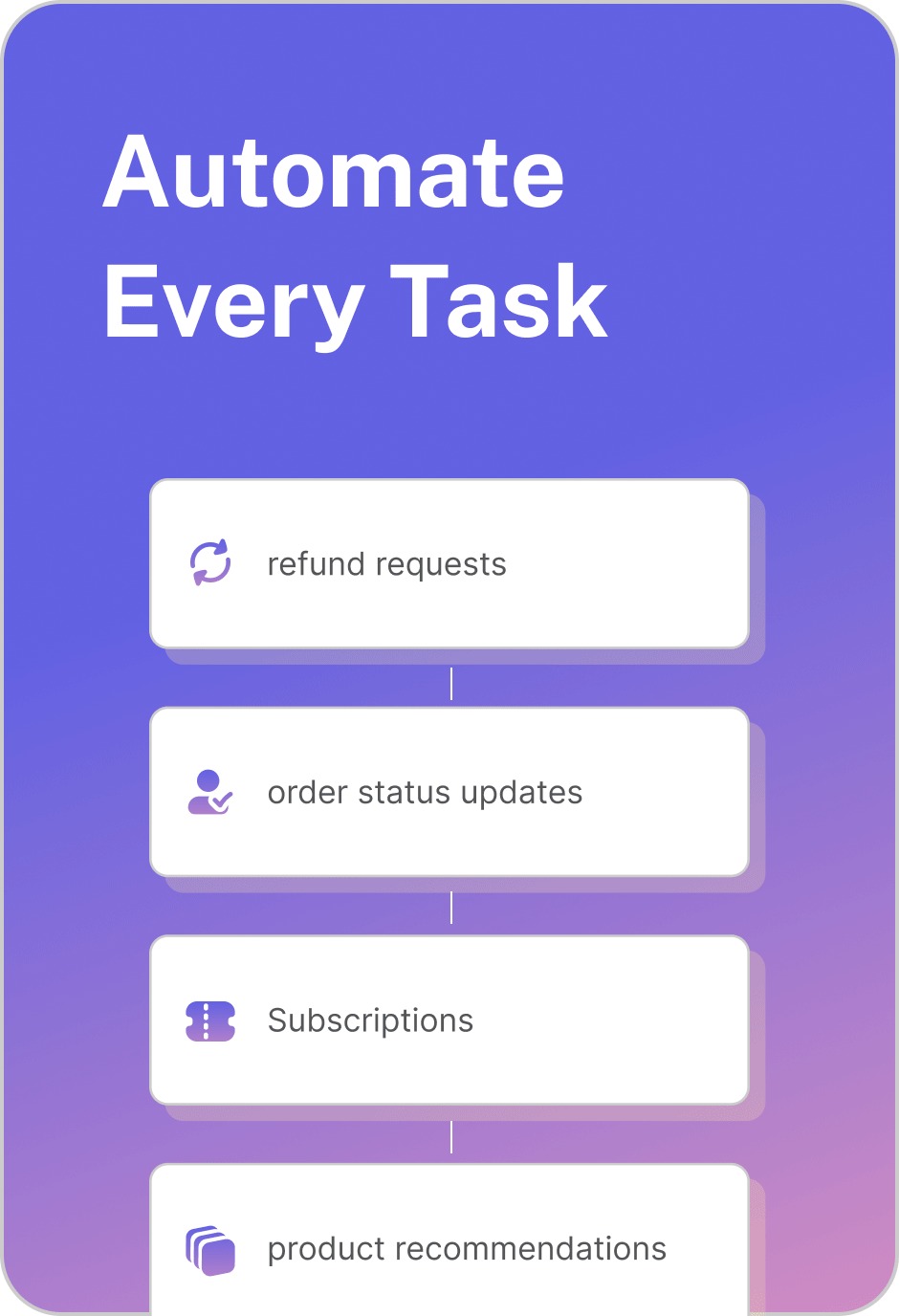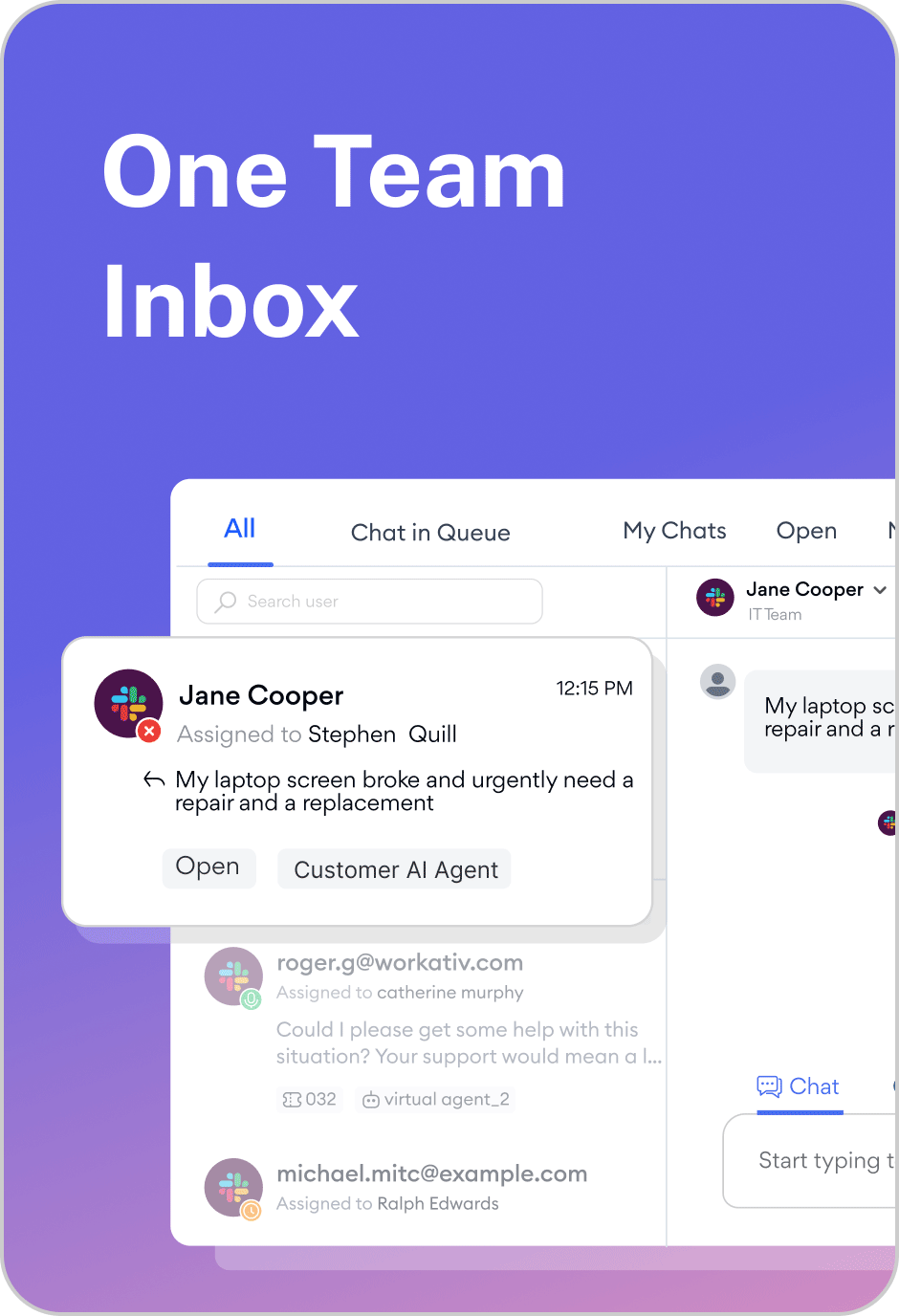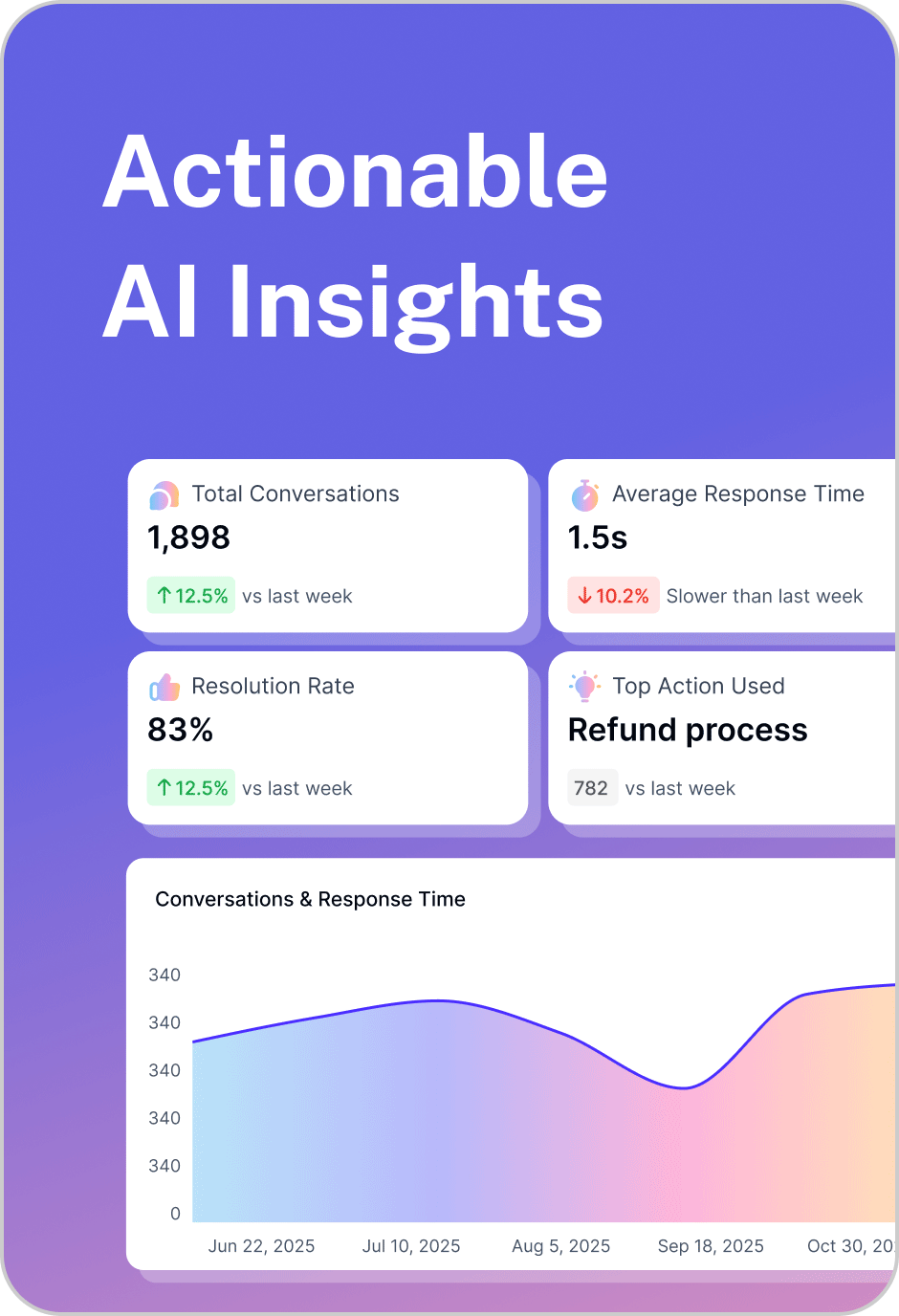
By understanding context and intent, AI agents deliver faster, more accurate, and personalized resolutions. This leads to shorter response times, fewer escalations, and a consistent experience across every interaction.
Lower operational costs
With repetitive and manual tasks automated, businesses can operate efficiently with smaller teams. AI agents enable 24/7 availability while reducing overhead associated with human support and training.
Continuous learning and improvement
Unlike static chatbots, AI agents learn from every conversation. They refine their understanding of user intent, adapt responses, and optimize workflows over time—becoming smarter with every interaction.
Scalability across departments
Whether managing IT requests, HR queries, or customer support, AI agents scale effortlessly across functions. They maintain consistent performance even during peak loads, ensuring business continuity.
Seamless integration
AI agents integrate deeply with CRMs, ERPs, HR systems, and ticketing platforms, creating connected workflows that eliminate silos and improve data accuracy.
The future: what’s coming in 2025–2026
The next two years will mark a defining era for conversational AI. As chatbots evolve into fully autonomous AI agents, we’re entering a phase where automation becomes proactive, context-aware, and outcome-driven.
Emerging trends shaping AI agents
Agent-to-agent communication
AI agents won’t work in isolation. Businesses will deploy multi-agent systems that collaborate, delegate, and solve problems together — from IT monitoring to cross-departmental workflows.
Specialized domain agents
Expect industry-tailored AI agents trained for specific domains like banking, healthcare, or HR. These pre-trained models will drastically reduce deployment time and boost accuracy.
Agent marketplaces
Soon, companies won’t need to build agents from scratch. Agent marketplaces will offer plug-and-play solutions for common business functions like lead qualification, ticket resolution, and data analysis.
Improved reasoning models
AI reasoning is set to leap forward. New LLMs will allow agents to plan, decide, and act with higher precision — performing complex, multi-step tasks that once required human oversight.
Agentic IDE integration
Coding assistants are evolving into autonomous developers. Agents will analyze requirements, generate code, test, and deploy software with minimal human input — accelerating product development cycles.
Voice-first agents
Voice is becoming the next frontier. Voice-first AI agents will dominate customer service and smart device ecosystems, making natural, human-like dialogue the default interaction mode.
Preparing for the shift
Businesses looking to stay competitive must prepare now.
Invest in strong data infrastructure to fuel reliable AI outcomes.
Implement governance frameworks to ensure ethical and auditable decision-making.
Upskill teams in agent design and management.
Start small, plan to scale, focusing on use cases with measurable ROI.
The move from chatbot automation to AI agency isn’t coming — it’s already here. Organizations that act early will define the next generation of intelligent, self-operating enterprises.
From conversations to intelligent action
The evolution from chatbots to AI agents marks a major shift in how businesses approach automation. Chatbots laid the groundwork by streamlining communication, but AI agents take it further — enabling systems that think, learn, and act across your organization.
As customer expectations grow and operational complexity increases, relying solely on scripted chatbots is no longer enough. AI agents bring the intelligence and autonomy needed to deliver real business outcomes — from resolving customer issues in seconds to automating workflows across departments.
For organizations aiming to move beyond reactive support and embrace proactive, outcome-driven automation, AI agents are the next step forward.
See how AI agents can transform your business operations, improve efficiency, and elevate customer experience.
Book a personalized demo to experience how intelligent agents can help your team move from conversation to action — effortlessly.
FAQs
Are AI agents replacing traditional chatbots?
Not entirely. Chatbots are still valuable for simple, high-volume interactions. However, many organizations are transitioning to AI agents to handle complex, multi-step workflows that require reasoning, context retention, and autonomy.
What is the difference between chatbots and AI agents?
Chatbots follow predefined scripts to respond to user queries, while AI agents use advanced reasoning and integrations to understand intent, make decisions, and perform real tasks. In short, chatbots talk, but AI agents act.
How do AI agents improve customer support operations?
AI agents integrate with tools like CRMs and ticketing systems to resolve issues end-to-end—for example, verifying data, updating records, or processing refunds—without human intervention, reducing response times and improving satisfaction.
Can small businesses benefit from AI agents?
Yes. Cloud-based AI agent platforms make enterprise-grade automation accessible to small and mid-sized businesses. They can automate repetitive workflows like lead management, order tracking, or HR queries at a fraction of the cost of manual labor.
What are the main challenges of implementing AI agents?
Common challenges include data quality, integration complexity, and AI governance. Businesses should start with pilot use cases, ensure clean data pipelines, and define clear escalation and compliance frameworks before scaling.
How fast is the AI agent market growing?
The global AI agent market is projected to grow from $5.1 billion in 2024 to $47 billion by 2030, at a 45% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This surge is driven by enterprise demand for automation beyond traditional chatbots.
What industries will benefit most from AI agents?
Industries such as retail, finance, healthcare, IT, HR, and e-commerce are leading adoption. Each benefits from agents that can handle domain-specific workflows like returns, approvals, ticket routing, and onboarding.
How can organizations prepare for AI agent adoption?
Companies should focus on data readiness, AI governance, and team upskilling. Starting with high-ROI use cases—like automating support tickets or sales qualification—creates a scalable foundation for broader deployment.
What’s next for AI agents in 2025–2026?
The next wave will bring multi-agent collaboration, domain-specific intelligence, and voice-first interfaces. AI agents will increasingly operate as autonomous digital coworkers, handling tasks across systems with minimal oversight.
Engage website visitors instantly,
resolve customer queries faster.
Do more than bots with pagergpt
About the Author

Senior content writer
Deepa Majumder is a writer who specializes in crafting thought leadership content on digital transformation, business continuity, and organizational resilience. Her work explores innovative ways to enhance employee and customer experiences. Outside of writing, she enjoys various leisure pursuits.