Evolution of AI Chatbots : From Scripts to Autonomous Agents
Discover how chatbots evolved into powerful AI agents that understand, act, and resolve issues and why now is the right time to upgrade.
Did you ever imagine it would be an all-inclusive experience for you while you chat with a conversational AI in the form of prompt-based AI platforms, and your cart items would be delivered at your doorstep? ChatGPT-powered shopping experiences make it happen in reality. With customers demanding such experiences, AI chatbots are no longer just script-based platforms, which can only talk and retract.
If you observe carefully, chatbots have never been so intelligent. They are now more action-based than script-based chatbots. Thanks to advancements in large language models, machine learning, and natural language processing.
Modern AI chatbots can integrate with apps, enable quick checkout, and fulfill your shopping. However, AI-powered chatbots don’t just automate shopping experiences. From service-based queries to internal employee issues, chatbots are wearing many hats to solve problems.
The evolution of chatbots plays a significant role in enhancing user experience. From a mere script-based tool to prompt-based AI applications that unleash real-world actions, chatbots have undergone many transitions. And platforms like pagergpt represent this next generation, powerful, LLM-driven AI chatbots built to deliver accurate, contextual, and cost-efficient customer support at scale.
Let’s walk through how we got here and what each stage of chatbot evolution unlocked.
A quick overview of the significant stages in chatbot evolution
Before we dive into each stage in detail, here is a simplified view of how chatbots evolved over the decades. Each era introduced new capabilities, solved old limitations, and paved the way for the AI agents we rely on today.
Chatbot / Agent | Year | Era | Characteristics |
ELIZA | 1966 | Rule-Based | First-ever chatbot; used pattern matching to simulate therapist-style dialogue. |
ALICE / A.L.I.C.E | 1995 | Rule-Based | AIML-powered template-matching chatbot; Loebner Prize winner. |
SmarterChild | 2001 | Rule-Based | AIM/MSN Messenger bot delivering quick facts, entertainment, and utility responses. |
Watson Assistant (early versions) | ~2011–2014 | Rule-Based | Script-driven enterprise chatbot built on Watson’s early dialog trees. |
Google Dialogflow | 2016 | NLP/ML | Intent-based NLP chatbot builder enabling more natural conversational flows. |
IBM Watson Assistant (ML era) | 2016 | NLP/ML | Added ML-driven intent detection and entity extraction for enterprises. |
Microsoft LUIS | 2017 | NLP/ML | NLP service for interpreting user intent; used for bot building in enterprise apps. |
Rasa (NLP framework) | 2017 | NLP/ML | Open-source ML-based chatbot framework with customizable pipelines. |
GPT-3 Chatbots | 2020 | LLM/Generative AI | First major LLM enabling human-like responses without manual intent mapping. |
ChatGPT (GPT-3.5/4) | 2022 | LLM/Generative AI | Popularized natural, multi-turn conversations; benchmark for generative chatbots. |
Google Bard (PaLM) | 2023 | LLM/Generative AI | Generative AI chatbot using Google’s PaLM models for reasoning and search. |
Anthropic Claude | 2023 | LLM/Generative AI | Safety-focused generative assistant with strong summarization and reasoning. |
OpenAI GPT-4.1 Agents | 2024 | AI Agents | Introduced advanced tool-calling and multi-step reasoning automation. |
Anthropic Claude 3 Agents | 2024 | AI Agents | Enterprise-safe agents with API calling and advanced context handling. |
Google Gemini 1.5 Agents | 2024 | AI Agents | Multimodal agents capable of document/image/video reasoning + actions. |
Microsoft Copilot Agents | 2024 | AI Agents | Agentic automation across Microsoft 365 apps with enterprise permissions. |
Cohere Command R/R+ Agents | 2024 | AI Agents | Retrieval-first enterprise agents for knowledge-heavy support workflows. |
pagergpt AI Agents | 2024–2025 | AI Agents | End-to-end support automation agents using LLM reasoning + RAG + integrations. |
Evolution: The history of AI chatbots
Let’s take a rundown on how chatbots have evolved and how they have shaped the way we work.
Rule-based chatbots (Early 2000s – 2016)
Rule-based chatbots relied on predefined scripts, decision trees, and keyword triggers. They didn’t understand language; they simply matched user input to preset patterns and delivered fixed responses. If a user phrased something differently from what the bot expected, the conversation broke. Some significant chatbots that emerged in this period include,
ELIZA (1966)
Created by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT, ELIZA was the first chatbot to use simple pattern-matching to simulate conversation. Its famous “DOCTOR” script reflected user statements back as questions. Although intentionally simple, many users mistakenly believed it understood them.
ALICE / A.L.I.C.E (1995)
Developed by Dr. Richard Wallace, ALICE used AIML to create thousands of hand-coded conversational templates. It pushed the limits of rule-based chat through structured pattern matching. ALICE won the Loebner Prize three times but still lacked true language comprehension.
SmarterChild (2001)
SmarterChild, created by ActiveBuddy, became a popular bot on AIM and MSN Messenger. It delivered fast, utility-focused answers like weather, sports scores, and trivia using scripted logic. Its success previewed the demand for later virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa.
Watson Assistant (early versions)
Early versions of IBM’s Watson Assistant relied heavily on dialog trees and scripted workflows. They were designed to help enterprises automate repetitive FAQs after Watson’s Jeopardy! Breakthrough. Despite being more structured than earlier bots, they still lacked real natural language understanding.
Limitations:
No reasoning or real comprehension
Could not handle varied phrasing or complex questions
No memory or context awareness
Extremely rigid and repetitive
Costly and time-consuming to maintain and update
Use cases:
Basic FAQ automation
Simple website customer support
Menu-driven chat interfaces
Call-center response deflection
NLP and machine learning chatbots (2016 – 2020)
NLP and ML chatbots introduced intent classification and entity extraction, enabling them to understand user intent rather than relying solely on fixed keywords. Businesses trained these bots using sample phrases so the model could identify patterns and map user queries to predefined intents, such as check_order_status or reset_password. This made conversations slightly more flexible, but the bots still followed structured dialog flows that had to be manually designed and maintained. Some chatbots that emerged in this period include,
Google Dialogflow (2016)
Developed by Google, Dialogflow became one of the most widely adopted NLP chatbot builders. It used intent detection and training phrases to help businesses build more natural conversational flows. While more flexible than rule-based bots, it still required extensive manual setup and training.
IBM Watson Assistant (ML versions, 2016 onward)
Watson’s later versions incorporated machine learning to improve intent recognition. Businesses could train the bot on sample queries to improve accuracy and reduce reliance on keywords. Despite these upgrades, conversations remained largely scripted.
Microsoft LUIS (2017)
LUIS (Language Understanding Intelligent Service) focused on interpreting user intent for enterprise applications. It allowed developers to build chatbot logic by training ML models on different utterances. However, LUIS lacked conversational depth and relied on manual dialog management.
Rasa (Open Source, 2017)
Rasa became a popular open-source framework for developers wanting full control over their chatbot’s NLP pipeline. It combined ML-based intent detection with customizable dialog policies and context tracking. Still, it required significant engineering effort and training data to maintain.
Limitations:
Required continuous training and data labeling
Struggled with ambiguous or complex queries
Dialog flows were still rigid and easily broke
Scaling required heavy maintenance and ML refining
Dependent on large intent libraries and structured flows
Use cases:
Customer support FAQs
Banking/telecom query routing
Appointment scheduling
Basic troubleshooting steps
Lead qualification flows
Generative AI and LLM Chatbots (2020 – 2023)
The reason why Generative AI and LLM-based chatbots have emerged is possibly that NLP bots are failing to understand the nuances of unpredictable conversations. Businesses faced rising customer expectations for open-ended, human-like interactions, and ML-driven systems could not handle nuance or multi-turn reasoning. This gap paved the way for LLM-based, generative chatbots — the next major evolution.
Generative AI chatbots used large language models (LLMs) that were trained on massive datasets to generate human-like responses in real time. Instead of relying on predefined intents, these bots understood context, inferred meaning, and produced flexible, free-form answers. This was the first time chatbots could hold natural, open-ended conversations without scripted dialog flows, making them far more potent than NLP-based systems.
Some great GenAI and LLM chatbots include,
GPT-3 & GPT-3.5 Chatbots (2020–2022)
Developed by OpenAI, GPT-3 introduced unprecedented capabilities in natural language understanding and generation. It allowed chatbots to interpret complex or ambiguous prompts without training on specific intents. GPT-3.5 later powered ChatGPT’s early versions, setting a new benchmark for conversational AI.
ChatGPT (2022)
Launched by OpenAI, ChatGPT became the first widely adopted consumer-facing AI assistant. It showcased how LLMs could carry multi-turn, human-like conversations across any topic. Its viral success demonstrated the potential for AI to transform customer support, education, and everyday productivity.
Are you keen to have ChatGPT streamline your customer support workflows? Know how to train ChatGPT on your own data and gain massive operational efficiency for your customer support.
Google Bard (PaLM-based, 2023)
Google introduced Bard using its PaLM and later PaLM 2 models to compete in the generative AI space. Bard provided conversational search, reasoning, and information summarization. It highlighted the rapid industry shift toward LLM-powered assistants.
Anthropic Claude (2023)
Claude, built by Anthropic, focused on safety-aligned generative AI with strong summarization and reasoning capabilities. Companies adopted Claude for support analysis, content generation, and knowledge interpretation. Its introduction accelerated competition in high-quality, enterprise-friendly chatbot models.
Limitations:
Prone to hallucinations (confident but incorrect answers)
No built-in access to business knowledge or customer data
Limited ability to execute actions (they could talk, but not do things)
Enterprise concerns around security, control, and compliance
Difficult to guarantee factual accuracy without external grounding
Use cases:
Complex troubleshooting explanations
Conversational FAQ handling
Knowledge summarization
Content generation and rewriting
Training and onboarding assistance
Autonomous AI Agents (2024 – Present)
While LLM chatbots were a major leap forward, businesses needed more than conversation — they required automation. LLMs could not take actions like creating tickets, processing refunds, fetching account data, or updating orders. This gap led to the rise of AI agents that combine LLM reasoning with tool-calling, RAG, integrations, and workflow automation — the next stage in chatbot evolution.
Autonomous AI agents combine LLM reasoning, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), tool calling, and workflow automation to not only understand user messages but also perform actions. Instead of responding solely with text, they connect to business systems — CRMs, ticketing tools, e-commerce platforms, HRIS, and internal APIs to execute tasks. These agents operate through multi-step reasoning, maintain context, and make decisions that go far beyond a traditional chatbot’s capabilities.
Some great examples of AI agents from this period include,
OpenAI GPT-4.1 / Agentic Models (2024)
OpenAI introduced agentic capabilities that allowed GPT models to call tools, reference external data, and automate workflows. These agent-driven features transformed the model from a conversational assistant into a task-oriented system. Businesses began using them for support, operations, research, and process automation.
Anthropic Claude 3 with Tool Use (2024)
Claude 3 expanded beyond text generation by incorporating tool-use functionality. It could call APIs, search knowledge bases, and complete structured tasks based on user intent. Its focus on safety and reasoning made it attractive for enterprise-grade automation.
Microsoft Copilot & Copilot Studio Agents (2024)
Microsoft Copilot evolved into a full agent platform through Copilot Studio, enabling organizations to build AI agents connected to internal data and Microsoft 365 apps. These agents automate tasks across Teams, Outlook, SharePoint, and Dynamics. With enterprise-grade permissions and identity controls, Copilot became a strong option for M365-driven workflows.
Google Gemini 1.5 Agents (2024)
Gemini introduced multimodal agent capabilities—interpreting text, images, documents, and even videos while performing structured actions. Its long-context reasoning enabled deep troubleshooting, analysis, and workflow execution. Gemini Agents pushed the boundaries of what an AI assistant could autonomously accomplish.
Cohere Command R / Command R+ Agents (2024)
Cohere released enterprise-focused agent models designed for retrieval-heavy tasks and operational workflows. These agents excelled at querying internal knowledge, summarizing systems, and powering complex customer support automation. Their emphasis on controllability made them ideal for regulated industries.
pagergpt AI Agents (2024–Present)
pagergpt represents the applied form of agentic AI specifically designed for customer support and business operations. It combines LLM reasoning with RAG, tool integrations, and automations to perform real tasks such as creating tickets, processing refunds, updating orders, routing constraints, and managing workflows. Unlike chat-only models, pagergpt focuses on accuracy, enterprise compliance (ISO, SOC2, HIPAA), and end-to-end resolution.
What Defines an AI Agent?
AI agents represent a major evolution beyond traditional chatbots. Unlike chatbots that only generate replies, agents are designed to take action and complete tasks end-to-end. A modern AI agent is defined by the ability to:
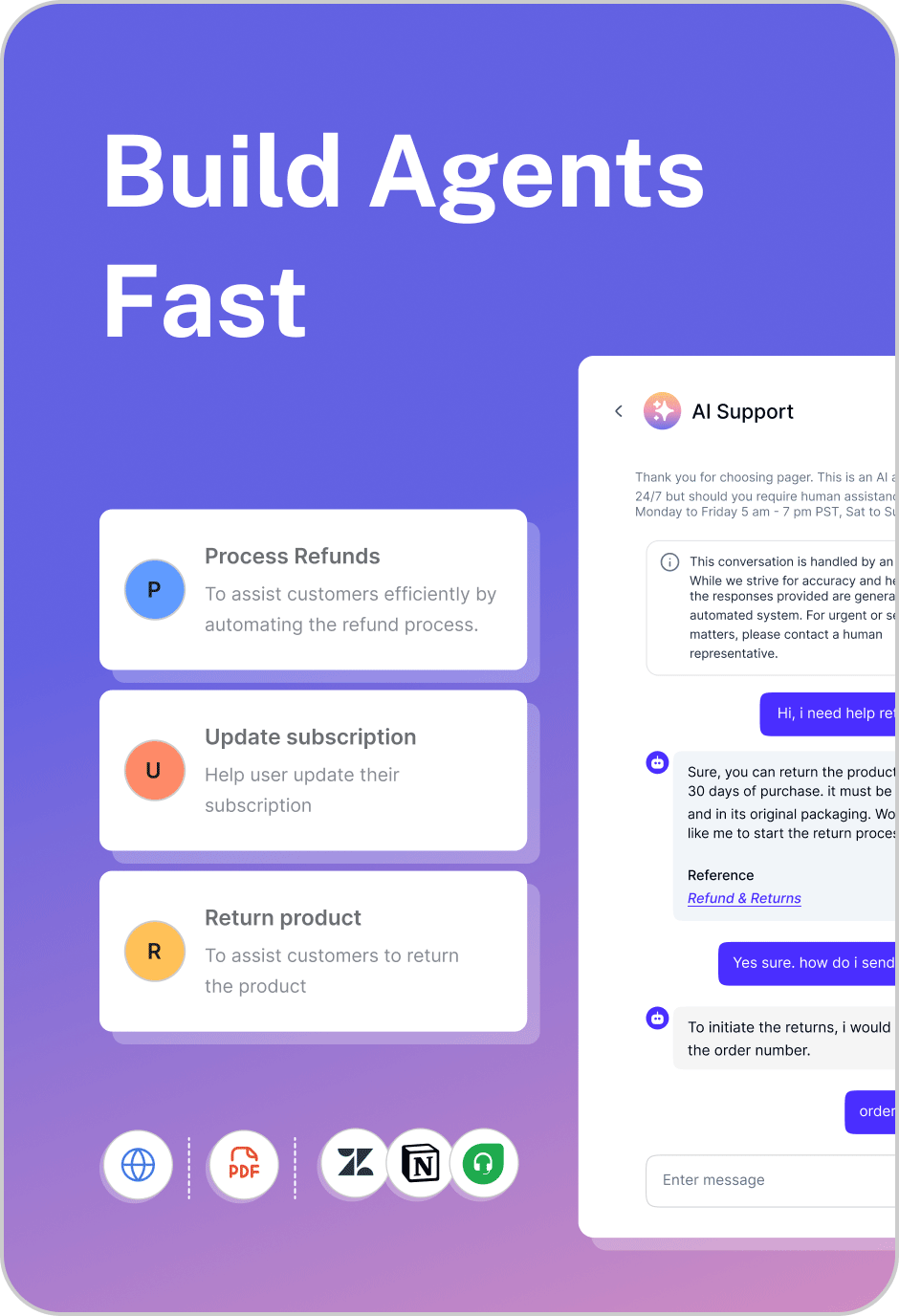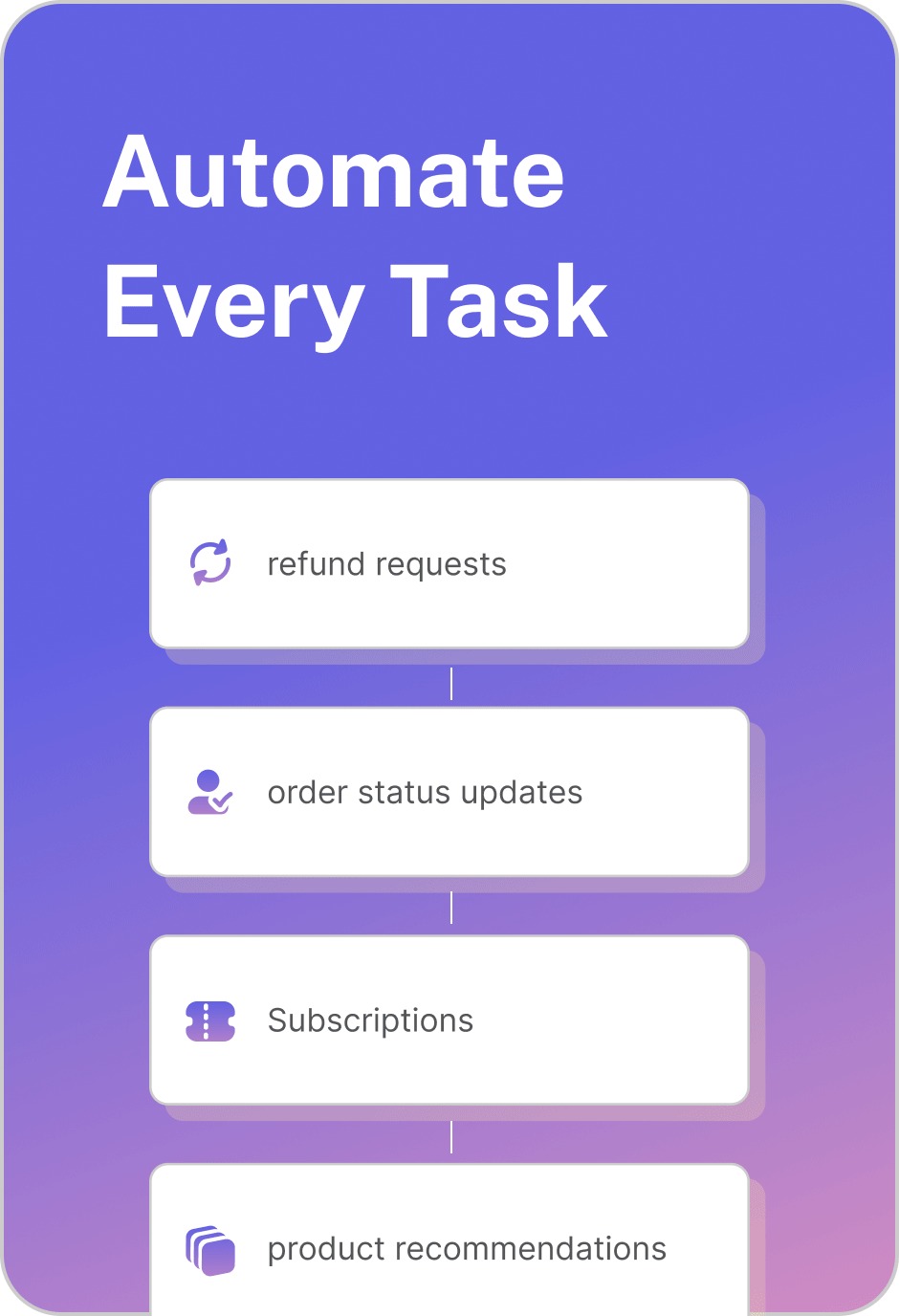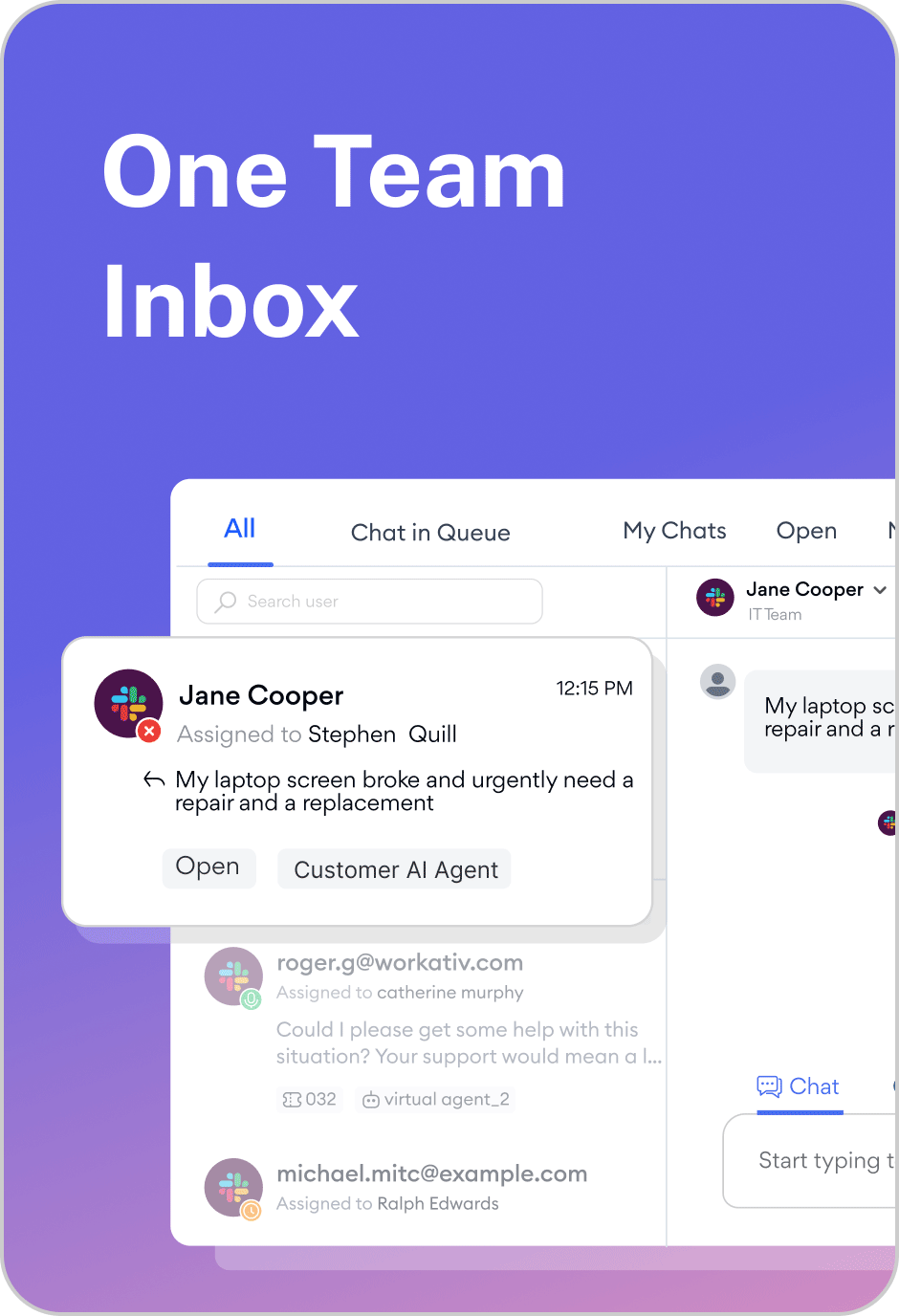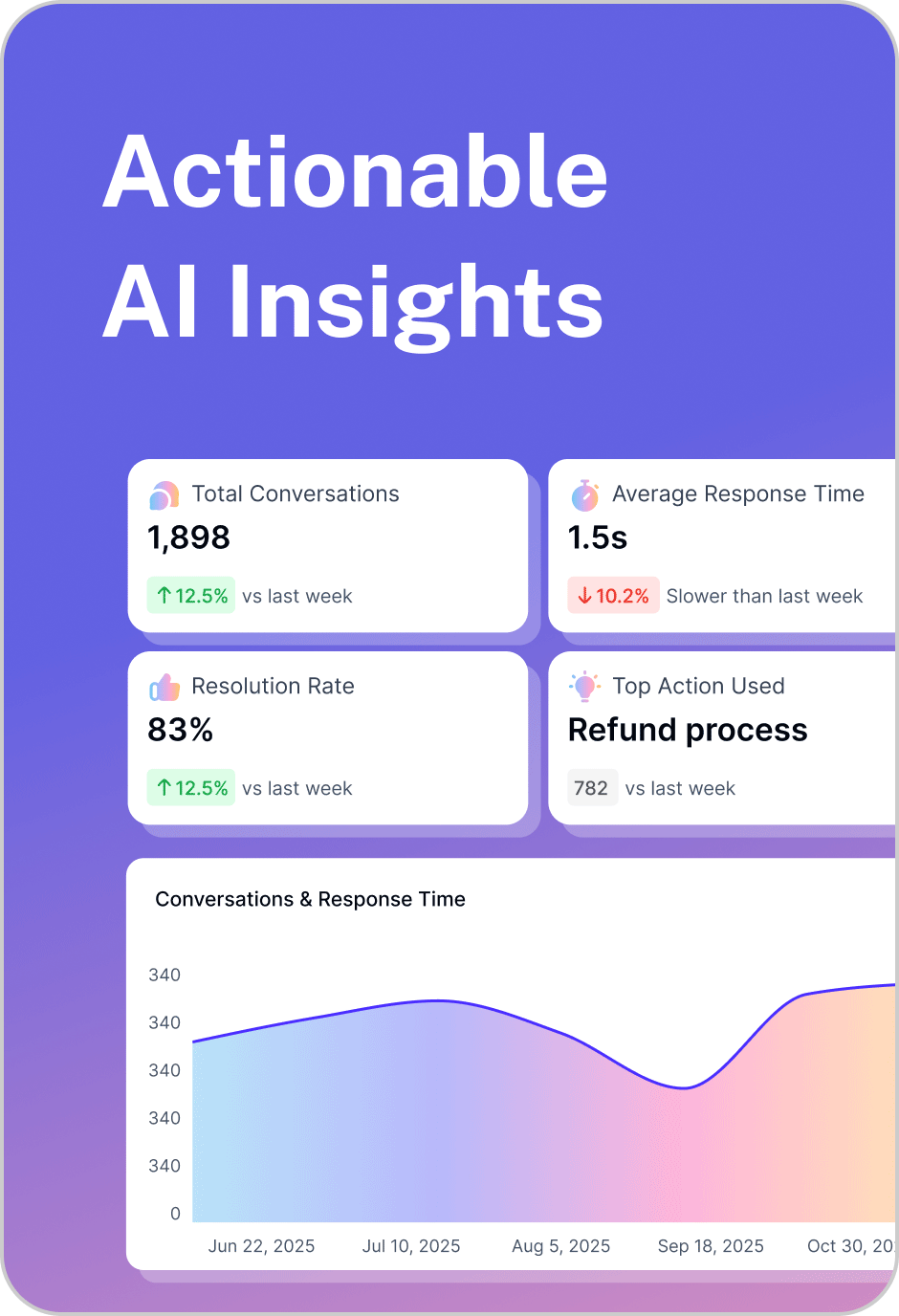
Perform real actions — not just answer questions, but execute workflows such as creating tickets, processing refunds, or updating orders.
Connect to apps and tools such as Zendesk, Shopify, Slack, HubSpot, and Salesforce to retrieve or update information.
Use RAG + real-time data to ground responses in accurate, current business knowledge.
Execute multi-step tasks, breaking a user’s request into a sequence of actions and completing them autonomously.
Understand user context across the entire conversation and adapt its responses accordingly.
Maintain memory, remembering earlier messages or user-specific details to avoid repetition.
Operate across channels such as web chat, WhatsApp, Messenger, Slack, and email for unified support.
Handle escalation smoothly, handing off to a live agent with full context when needed.
AI agents aren't just conversational—they are operational systems capable of doing real work.
Why this era matters
This new era of AI agents is transformative because:
AI agents ≠ chatbots — they perform tasks, make decisions, retrieve data, and resolve issues.
They drive operational efficiency, offloading repetitive workloads so teams can focus on complex cases.
They reduce support costs by automating high-volume, predictable requests.
They improve CSAT through instant resolution, personalized responses, and round-the-clock availability.
They scale effortlessly, supporting thousands of customers simultaneously without additional headcount.
This shift from conversational bots to action-oriented agents is why AI agents are quickly becoming mission-critical for modern support and operations.
The key innovations shaping the chatbot evolution
These innovations transformed chatbots into intelligent AI agents capable of real actions and accurate, automated support.
LLM reasoning and tool calling
LLMs enable agents to think through requests and perform real actions like creating orders, fetching tickets, or processing returns.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
RAG grounds responses in verified knowledge, eliminating hallucinations and improving accuracy.
Multimodal AI
Agents can understand images, read documents, and analyze screenshots to troubleshoot more effectively.
Reusable personas and templates
Prebuilt personas let businesses instantly adapt agents for industries like e-commerce, SaaS, healthcare, finance, and HR.
Omnichannel deployment
Agents work across WhatsApp, Messenger, Slack, and web widgets, ensuring a unified customer experience across all channels.
Analytics and autonomous learning
Agents learn from session insights, deflection data, and intent patterns to continuously improve performance and coverage.
How pagergpt represents the next evolution of AI chatbots
pagergpt is built for the modern era of AI agents, explicitly designed to automate customer support and operational workflows end-to-end. It offers enterprise-grade security, such as ISO, SOC2, HIPAA, and GDPR, and supports multi-source training, pulling knowledge from websites, PDFs, Confluence, Zendesk, Freshdesk, and more. With tool calling and deep app integrations, pagergpt can perform real actions like refunds, ticket routing, and order lookups. It includes a live agent inbox, advanced analytics, and a no-code builder with developer extensibility, making it powerful yet easy to deploy.
Advantages over older chatbot approaches
No intent training needed
pagergpt works out of the box without requiring teams to create or maintain intent libraries.
Handles natural language variations
It understands multiple ways of asking the same question, so conversations don’t break with unexpected phrasing.
Easy to maintain
The system automatically updates its responses as your knowledge sources change, reducing manual upkeep.
Higher accuracy with RAG
pagergpt delivers more reliable answers by grounding responses in real-time data and approved documentation.
Lower operational costs
By automating repetitive, high-volume tasks, pagergpt reduces the workload on human agents and decreases support costs.
Faster time-to-value
Businesses can deploy functional AI agents within hours instead of spending weeks building flows or training models.
Where AI chatbots are headed and why now is the time to upgrade
The evolution of chatbots has gone through four major eras, from simple rule-based responders to NLP-driven bots to generative LLM chatbots, and now to fully autonomous AI agents. Each stage unlocked new capabilities, but today’s customers expect more than answers; they expect real-time, intelligent, and action-driven support that solves problems instantly.
This is why the shift to AI agents is accelerating and why platforms like pagergpt represent the next step in this evolution. pagergpt combines LLM reasoning, RAG accuracy, deep integrations, and workflow automation to deliver support that doesn’t just respond but resolves.
If you're ready to move beyond traditional chatbots and embrace the future of AI-driven support, now is the time.
FAQs
How have chatbots evolved over the years?
Chatbots have progressed from rule-based scripts to NLP-driven bots, then to generative LLM chatbots, and now to autonomous AI agents capable of taking actions and resolving tasks.
What is the difference between a chatbot and an AI agent?
A chatbot mainly provides responses, while an AI agent can understand intent, access real-time data, call tools, and complete multi-step workflows to solve problems end-to-end.
Are LLM chatbots better than rule-based bots?
Yes, LLM chatbots understand natural language, handle variations, and provide more flexible, human-like responses compared to the rigid, predefined behavior of rule-based bots.
What technologies power modern AI chatbots?
Modern systems rely on large language models (LLMs), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), tool calling, vector search, multimodal reasoning, and API integrations.
Why are more companies adopting AI agents?
AI agents automate repetitive tasks, reduce support costs, improve response times, and deliver more accurate, personalized support helping businesses scale without additional staffing.
Engage website visitors instantly,
resolve customer queries faster.
Do more than bots with pagergpt
About the Author

Senior content writer
Deepa Majumder is a writer who specializes in crafting thought leadership content on digital transformation, business continuity, and organizational resilience. Her work explores innovative ways to enhance employee and customer experiences. Outside of writing, she enjoys various leisure pursuits.