12 Real-world examples of AI agents
Curious what AI agents actually do? Discover how AI agents are streamlining support, sales, HR, etc. See 12 practical use cases businesses are already using today.
AI agents are the buzz right now and for good reason.
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, says, “AI agents will become the primary way we interact with computers in the future. They’ll be able to understand our needs and preferences, and proactively help us with tasks and decision-making.”
Gartner predicts that by 2028, 33 % of enterprise applications will embed agentic AI, and up to 15 % of day-to-day decisions will be made autonomously.Meanwhile, McKinsey estimates that generative AI–driven agents, when scaled across functions, could help unlock $2.6–4.4 trillion in annual value across industries.
Let’s explore how AI agents are reshaping industries — with real-world examples, architectural insights, implementation best practices, challenges, and what’s next for this rising paradigm.
What are AI agents?
An AI agent is an autonomous AI system designed to perceive its environment, reason through information, and take actions toward achieving specific goals — with minimal human supervision. Unlike traditional chatbots that follow pre-set scripts or keyword triggers, AI agents can plan, decide, and execute tasks dynamically based on context and intent.
While a chatbot might answer “What’s my order status?” from a fixed database, an AI agent can fetch the order, analyze logistics data, and initiate a refund or escalation — all on its own.
Key characteristics of agentic AI systems:
Reasoning: Evaluate multiple options to find the best solution.
Autonomy: Perform actions or make decisions without manual input.
Goal pursuit: Continuously optimize behavior to reach desired outcomes.
In essence, agentic AI transforms static assistants into intelligent, adaptive digital coworkers.
How AI agents work
At their core, AI agents operate through a layered architecture that mirrors human cognition — perceiving, reasoning, and acting autonomously. This framework allows them to interpret context, make decisions, and execute tasks across complex workflows.
Input & perception layer
Agents begin by interpreting user input or data using natural language processing (NLP) and contextual parsing. This helps them understand intent, entities, and relevant context before taking any action.
Cognition layer
Once the query is understood, the reasoning engine analyzes goals and plans the optimal response.
The planner determines what needs to be done.
The executor handles decision sequencing and coordination.
The memory component ensures continuity across interactions — crucial for multi-turn or long-running conversations.
Action layer
Finally, the agent performs tasks through tool-calling — connecting to CRMs, ticketing systems, or APIs to fetch data, update records, or complete workflows. It then generates the final response or triggers a follow-up action.
Key features of modern AI agent architecture
Tool-calling for external actions: Execute real operations in tools like Zendesk, Slack, or Salesforce.
Memory and context retention: Maintain awareness across sessions for coherent, human-like interactions.
Multi-agent collaboration: Planner, executor, and evaluator agents can work together in a shared system.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Combine knowledge retrieval with LLM reasoning to ensure factual, domain-specific responses.
Most next-gen agentic AI systems seamlessly blend reasoning, memory, and tool use — making them self-improving digital coworkers that learn and adapt with every interaction.
Types of AI Agents

AI agents are of different types, like simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, learning agents, hierarchical agents, and multi-agent systems. Let’s discuss each of them with examples.
Simple reflex agents
These agents follow basic if-this-then-that logic. They respond directly to current conditions without considering past context. For example, a motion-sensor light turns on when it detects movement and turns off after a set time of inactivity.
Model-based reflex agents
Compared to simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents can perceive the world using internal models and make autonomous decisions despite missing critical information.
For example, a self-driving car approaching an intersection might not see the traffic light clearly due to fog or glare. But it can still decide to slow down or stop.
Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents are programmed to act toward specific goals. This means goal-based agents can understand complex scenarios and make autonomous decisions to achieve a goal.
For example, a smart budgeting app that adjusts your spending limits based on your savings goal is an example of a goal-based agent.
Utility-based agents
Utility-based agents assess multiple possible outcomes and select the one with the highest value or efficiency.
Resource-allocating systems, for example, use utility-based agents to optimize energy use, balancing machine use and production goals.
Learning agents
Unlike preprogrammed agents that work only using predefined knowledge, learning agents improve over time by learning from past experiences and feedback loops. They can adapt to new situations without needing to be reprogrammed.
For example, a virtual keyboard like Gboard learns how you type and customizes predictions based on your writing style, commonly used words, and corrections.
Hierarchical agents
Hierarchical agents operate in a tiered structure where higher- and lower-level agents collaborate to achieve a common goal. They break down complex tasks for better coordination.
For example, hierarchical agents in content creation workflows ensure quality by automatically overseeing the entire process, generating drafts, and editing final content.
Multi-agent system
A multi-agent system is built by multiple combinations of autonomous agents working together in the same environment. Each agent can handle a specific task and coordinate to achieve a shared goal or work independently when needed.
For example, in an employee support setup, one agent can handle IT issues, another can answer HR questions, and a third can manage access requests, all working together to resolve problems faster.
Top 12 AI agent examples in 2025
Research reveals that the AI agents market was valued at $3.84B in 2024 and is expected to grow to $51.58B by 2032, at a CAGR of 38.5%.
To help you see where AI agents are already making an impact, here are 12 real-world examples across teams and industries.
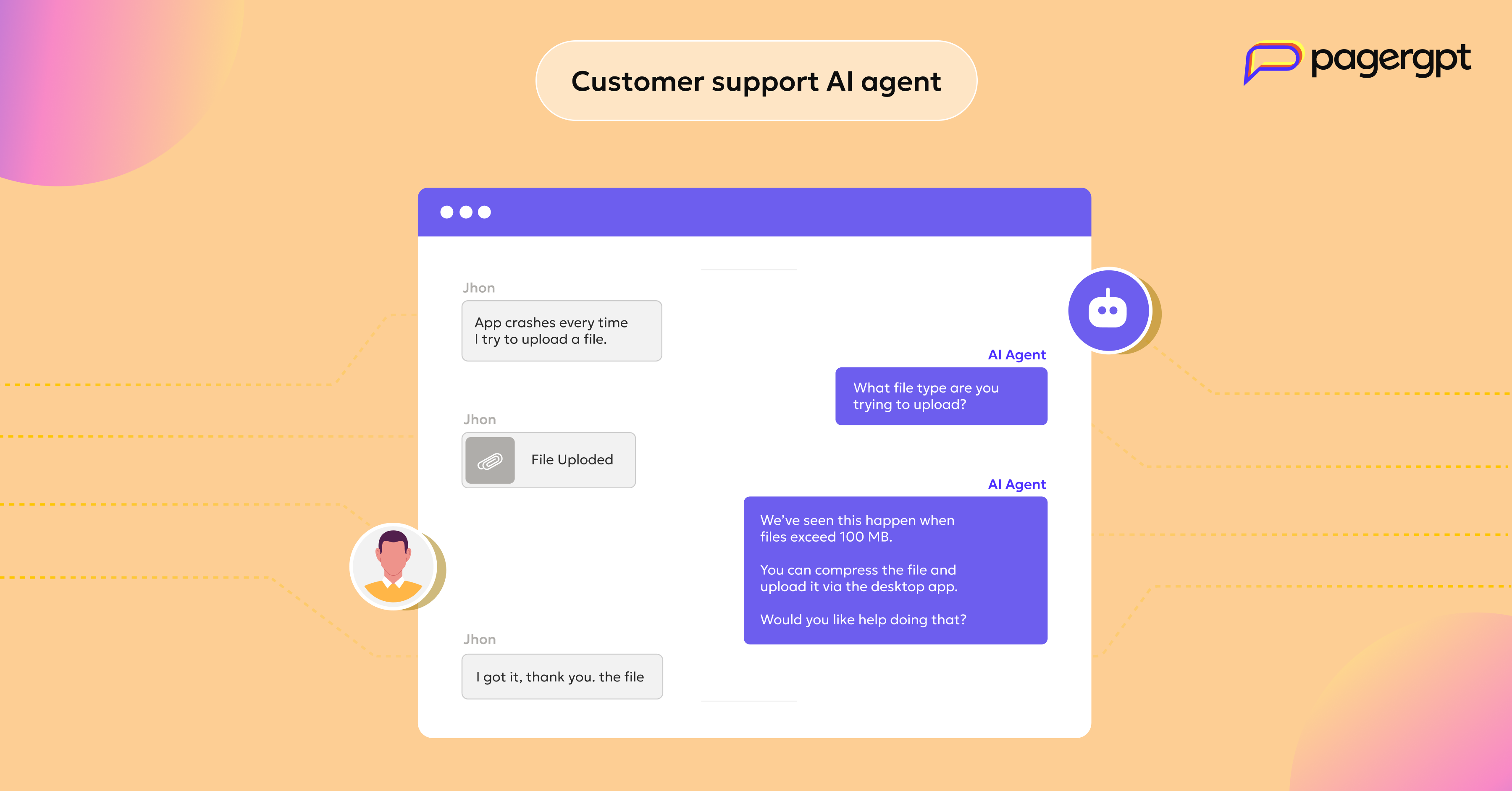
Customer support AI agent
Customer support AI agents will help you improve CSAT scores, enhance customer engagement, reduce the workload of human agents, and resolve customer queries at scale.
With platforms like pagergpt, you can build and deploy AI agents that fit right into your existing workflows and start delivering value from day one.
Here’s how customer support AI agent can automate customer support:
Auto-resolve common queries like FAQs, billing issues, order tracking, and cancellations
Provide multilingual support to engage customers globally.
Automatically route tickets to the right team based on query type or priority.
Guide new users through the product onboarding
Offer deep analytics on resolution times, satisfaction scores, and query types
Analyze customer feedback to detect sentiment and spot friction points
Schedule follow-up support calls based on customer needs or agent availability
Lead capture AI agent
Let’s say hundreds of potential leads visit your website every day. If you’re not engaging them instantly, you're likely losing high-intent prospects and revenue. Lead capture AI agents solve this for you.
Using pagergpt, you can build a lead capture AI agent that can:
Greet visitors with personalized prompts.
Collect and validate lead data like name, email, phone, company name, and size.
Push leads directly into your CRM or sales workflow.

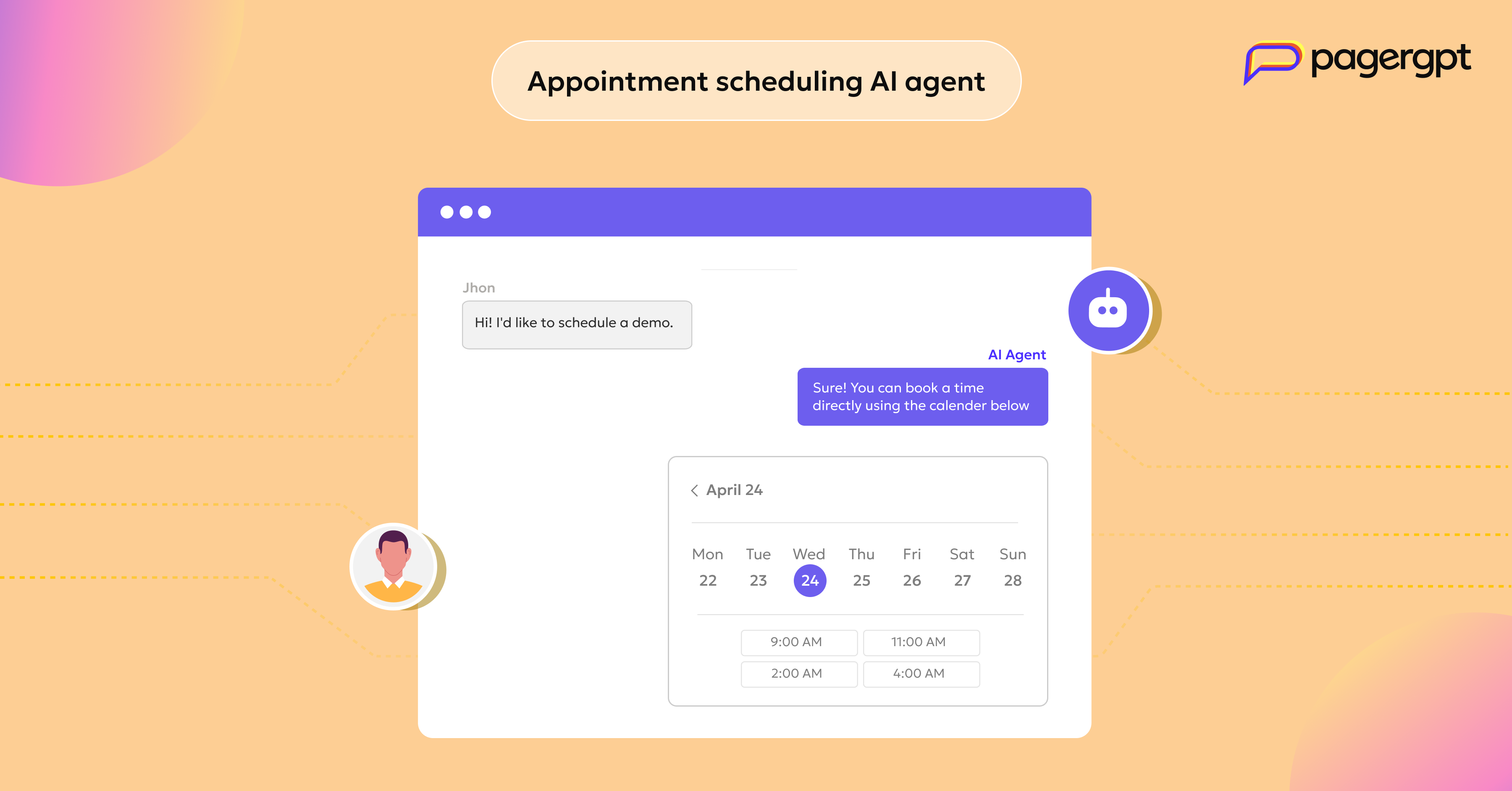
Appointment scheduling AI agent
Scheduling a meeting should be an easy task, but it can quickly become a nightmare with back-and-forth emails, time zone confusion, and constant rescheduling. Appointment scheduling AI agent makes scheduling a breeze.
Using pagergpt, you can build an appointment scheduling AI agent that can:
Find and book available meeting slots.
Sync with calendar tools like Google or Outlook.
Send reminders and follow-ups.
Handle rescheduling and cancellations.
Adjust for time zones automatically.
Sales inquiry AI agent
When website visitors ask about your pricing, features, or a demo, they show clear buying intent. The faster you respond, the better your chances of converting them. In fact, a study shows that 78% of B2B buyers go with the vendor that replies first.
Sales inquiry AI agents built with pagergpt can:
Answer product, feature, and pricing queries in real time.
Recommend plans or solutions based on the use case.
Share relevant content like demos or case studies.
Gauge buyer intent through conversations.
Route high-intent leads to sales reps.
Marketing AI agent
Marketing AI agents help automate, personalize, and scale campaign efforts across channels. Here’s how they help:
Segment users based on behavior, demographics, and past interactions.
Personalize email campaigns, web experiences, and ad content at scale.
Support account-based marketing (ABM) by identifying important companies visiting your site and showing them relevant content.
Monitor social media to track brand mentions, customer feedback, and competitor activity in real-time.
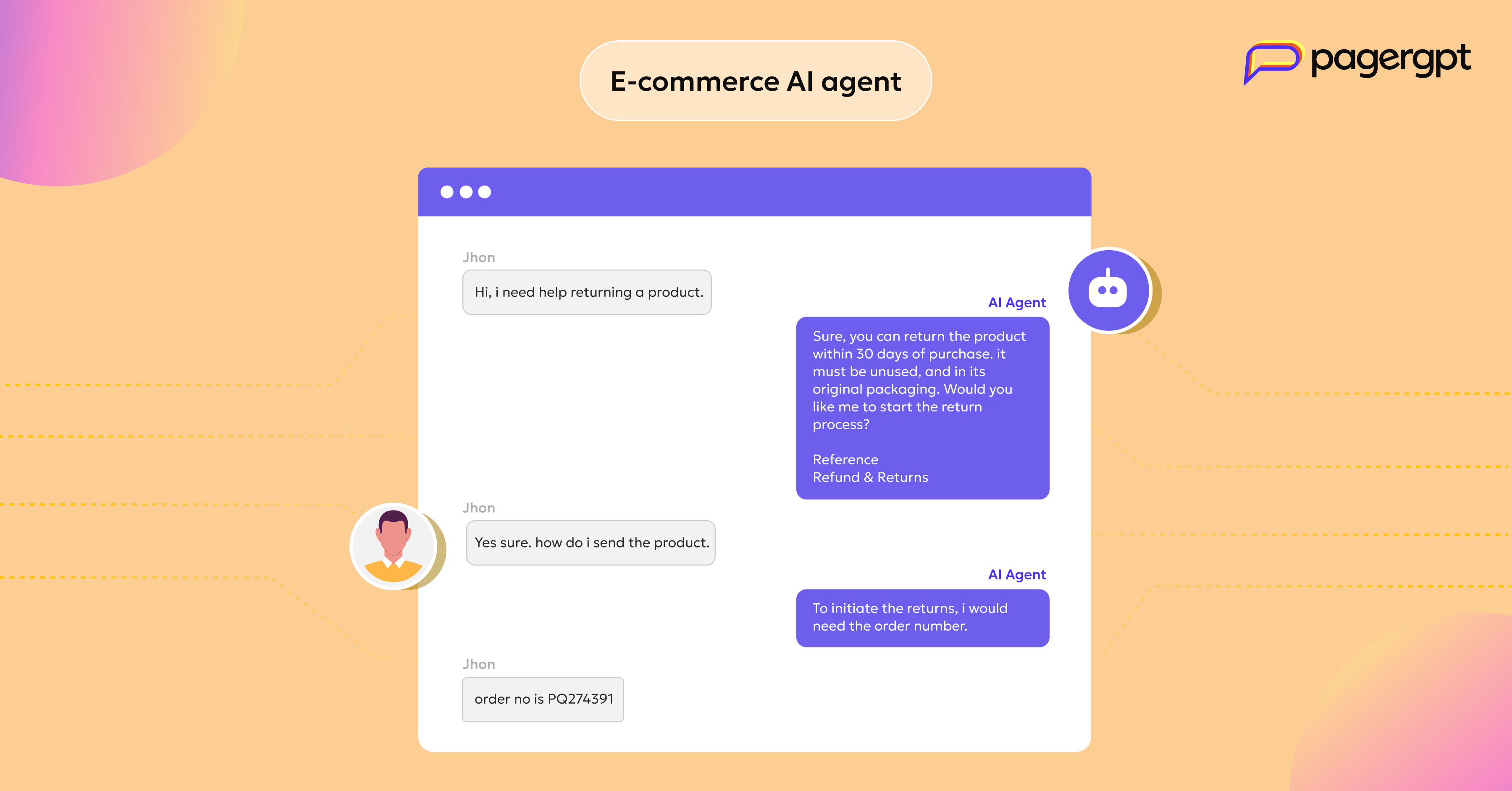
E-commerce AI agent
Most e-commerce businesses lose sales because of poor customer experience. According to Qualtrics, 80% of customers have switched brands after just one bad experience.
If you're looking to fix that and turn more browsers into buyers, implementing an e-commerce agent would be the right move.
With pagergpt, you can create one trained on your store data and built to assist customers in real-time. Here’s what it can do for you:
Help customers place orders through chat.
Provide real-time shipping updates.
Recommend products based on browsing or purchase history.
Send cart abandonment reminders.
Assist with returns and refunds.
Recommendation AI agent
A McKinsey report reveals that 71% of customers expect personalized experiences and 76% express frustration when they don’t receive them.
So, if you want to engage more customers with personalization, a content recommendation AI agent is one of the simplest ways to make it happen.
Here’s what it can do:
Suggest products or resources based on past behavior and similar user profiles.
Recommend upsell or cross-sell items.
Personalize homepage, emails, and app feeds.
Improve the discoverability of high-margin products.
Continuously learn from user interactions to improve relevance.
IT support AI agent
IT support AI agents take the pressure off your helpdesk by handling repetitive issues and reducing downtime. They improve employee experience, speed up resolutions, and offer real-time support across tools your team already uses.
They can take care of tasks like:
Resetting passwords and unlocking accounts
Guiding users through common troubleshooting steps
Automatically triaging and routing tickets to the right team
Sharing system setup docs and how-to guides
Responding instantly through Slack, Teams, or chat
HR support AI agent
HR AI agents take all the grunt work, so your HR team can focus on what actually matters, like improving company culture, devising retention strategies, and workforce planning.
HR support AI agents can step in to handle things like:
Answering questions about leave, payroll, and policies
Guiding new hires through onboarding
Automating leave requests and approvals
Sending reminders for timesheets, document uploads, and compliance tasks
Fraud detection AI agent
Banking and finance industries can drastically reduce turnaround time, minimize human errors, and improve operational efficiency by employing fraud detection AI agents in their workflows.
What a fraud detection AI agent can do:
Monitor transactions for anomalies
Flag suspicious login or payment behavior
Trigger account verification flows
Alert risk or compliance teams
Learn from flagged cases to improve detection
Healthcare AI agent
Healthcare AI agents assist with patient interactions and basic medical support, so staff can focus more on patient care.
Here’s what a healthcare AI agent can do:
Book, reschedule, and cancel appointments
Answer common health or clinic-related questions
Send reminders for medication and follow-ups
Help with patient intake before visits
Triage symptoms and route to the right department
AI agents for dynamic pricing
Dynamic pricing AI agents help businesses stay ahead by adjusting real-time prices to maximize revenue and stay competitive.
Take the travel industry, for example you want to make the most of high-demand periods like holidays and peak seasons. But manually adjusting prices involves a lot of guesswork.
Dynamic pricing AI agents take the pressure off by automating this process. They can:
Change prices based on demand and competitor activity
Apply discounts or surge pricing in real time
Test different price points with A/B testing
Forecast pricing trends using historical data
How to implement an AI agent
Building an AI agent is no longer a complex, developer-only task. With modern no-code platforms like pagergpt, businesses can design, train, and deploy autonomous agents that perform real tasks across customer support, IT, HR, or sales — securely and at scale.
Here’s a simple step-by-step framework for implementing your first agentic AI system:
Define the business goal
Identify what you want the agent to accomplish — for example, resolving 60% of customer queries, automating HR requests, or qualifying leads. Clear objectives help decide which workflows and tools your agent will need to access.
Choose the right agent type
Decide between a support, sales, HR, IT, or finance agent based on your domain. For complex environments, use multi-agent systems where planner, executor, and evaluator agents coordinate tasks.
Train your agent with data
Feed your agent structured and unstructured sources such as website content, knowledge base articles, documents, or help-desk FAQs. Platforms like pagergpt allow multi-source training via file uploads, URLs, or integrations with tools like Confluence or Zendesk.
Connect external tools and apps
Enable tool-calling so the agent can act — not just answer. Integrate CRMs, ticketing systems, HR software, or Slack for executing real workflows like creating tickets or sending follow-ups.
Add reasoning and guardrails
Configure the reasoning chain (planner + executor) so your agent can plan multi-step actions. Use guardrails such as RBAC, PII masking, and action limits to ensure safe and compliant behavior.
Test and refine with live interactions
Run simulated chats or internal pilots to test accuracy, tone, and workflow success. Track whether the agent retrieves the right data and performs the expected actions.
Deploy and monitor performance
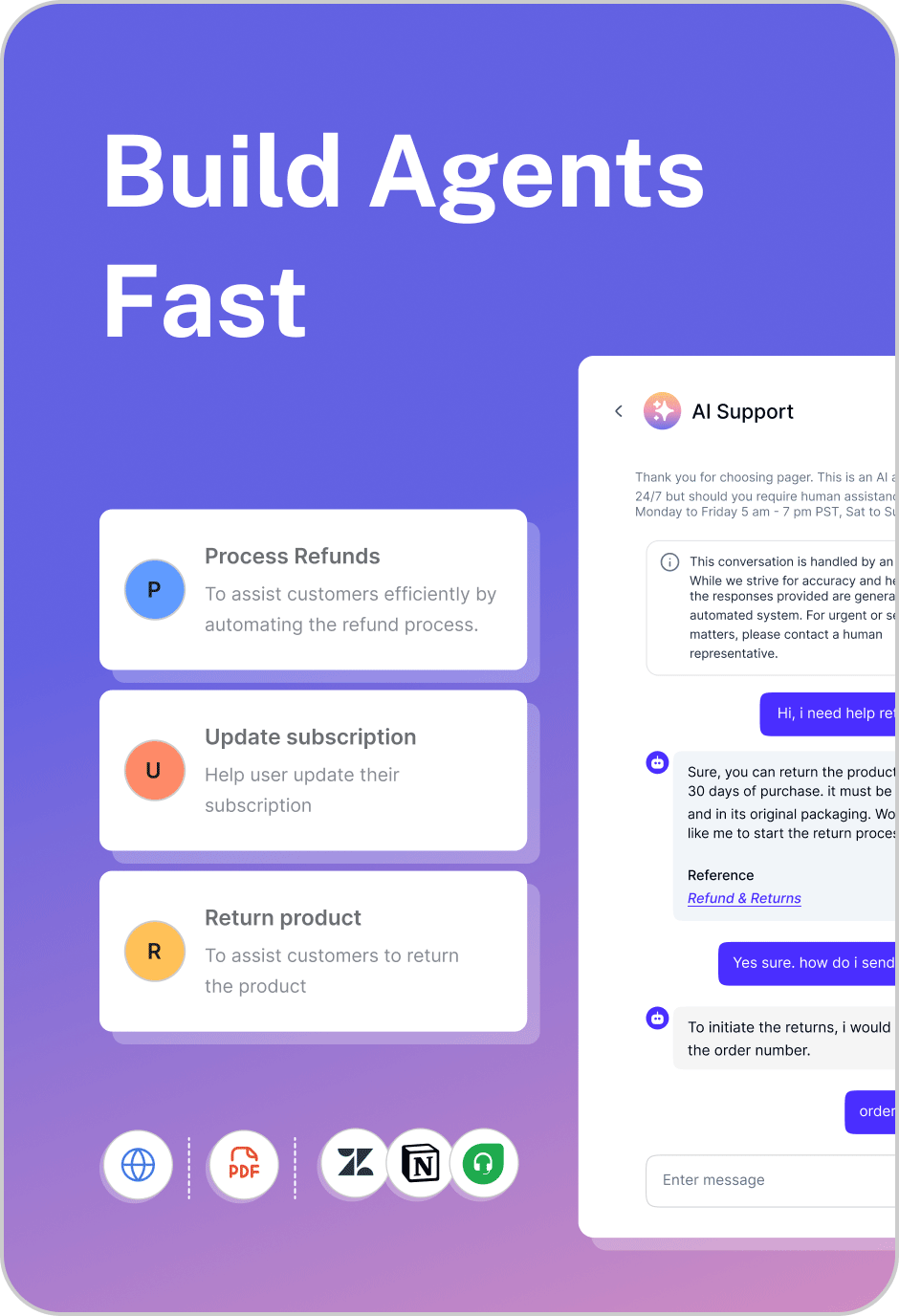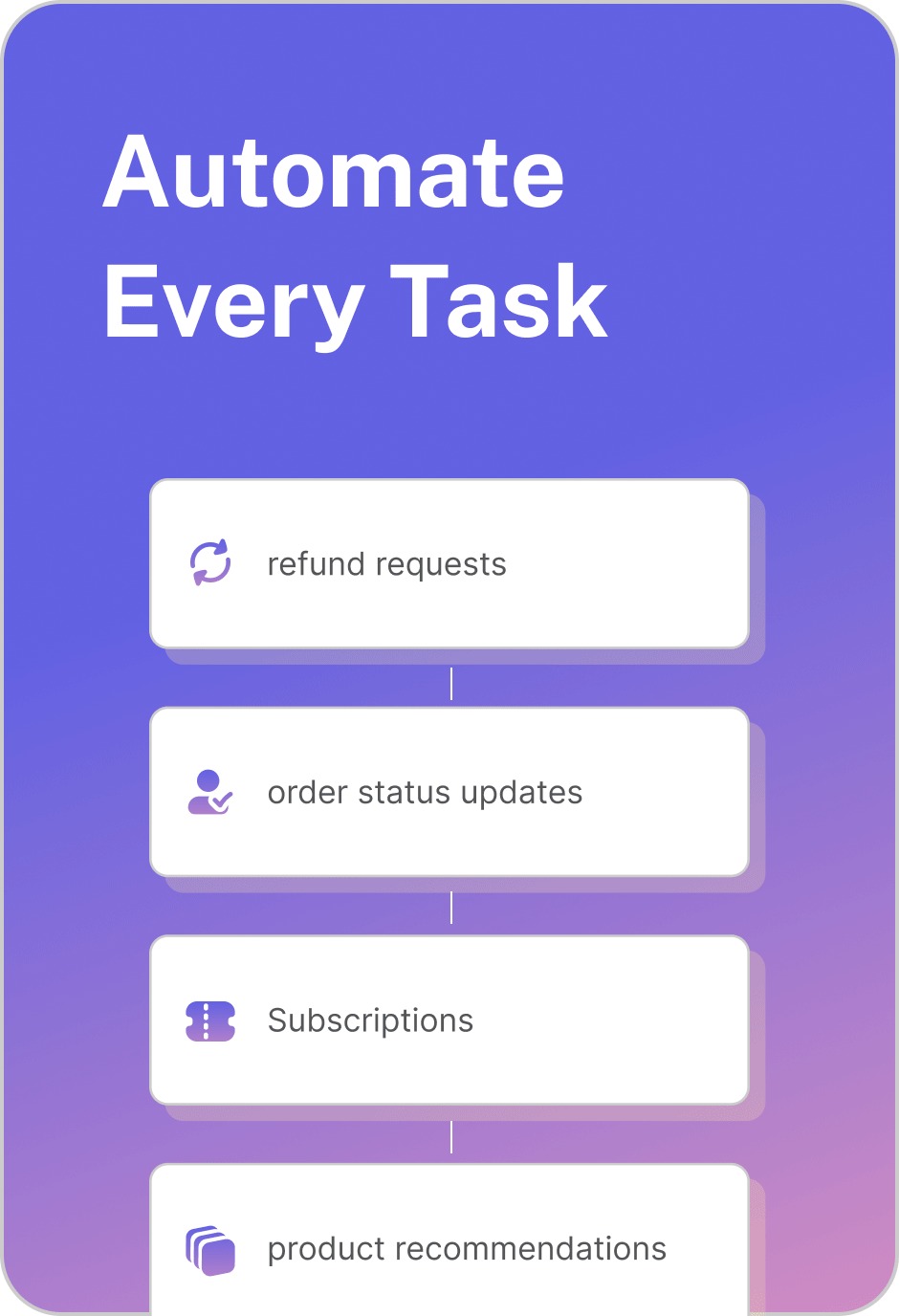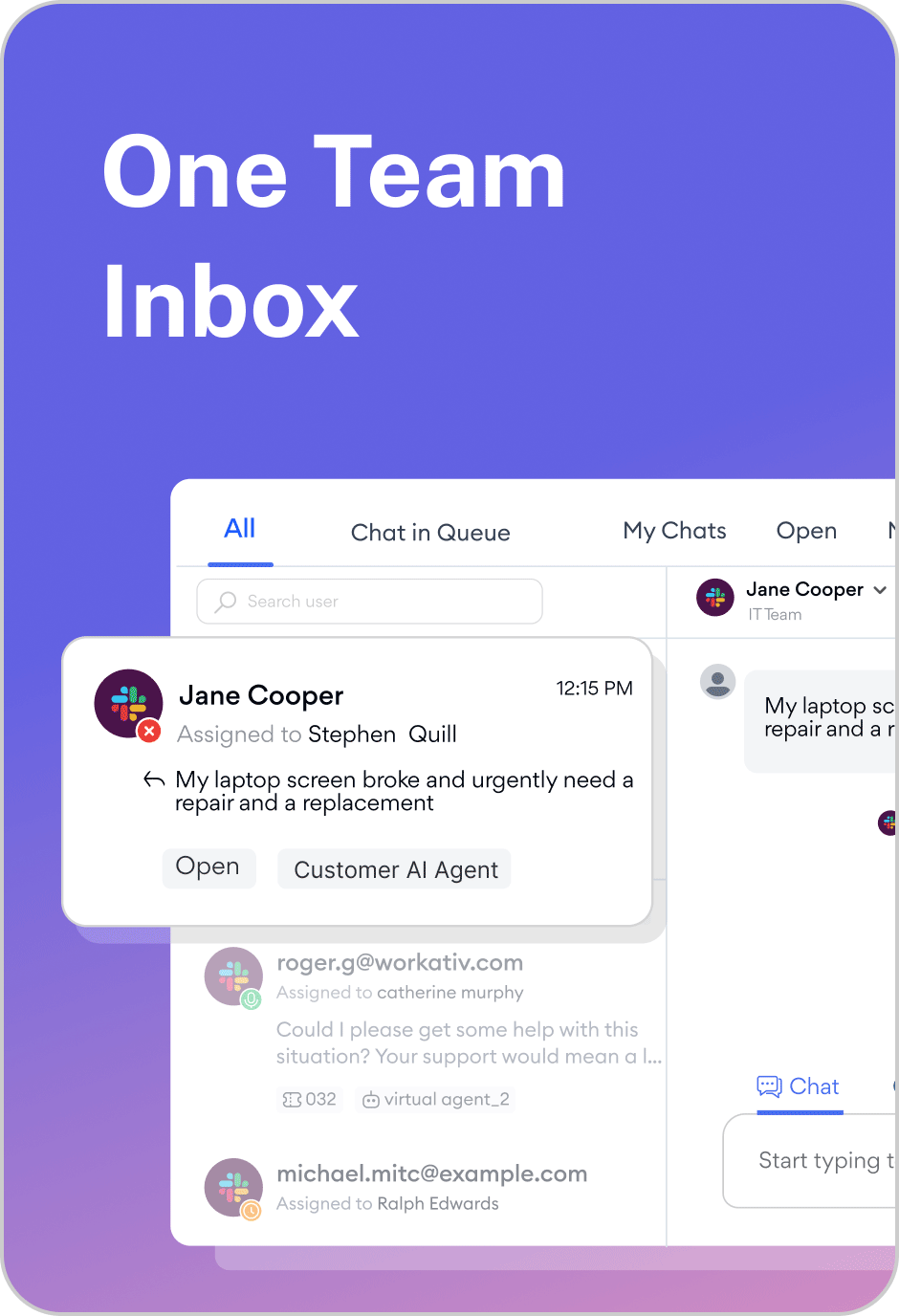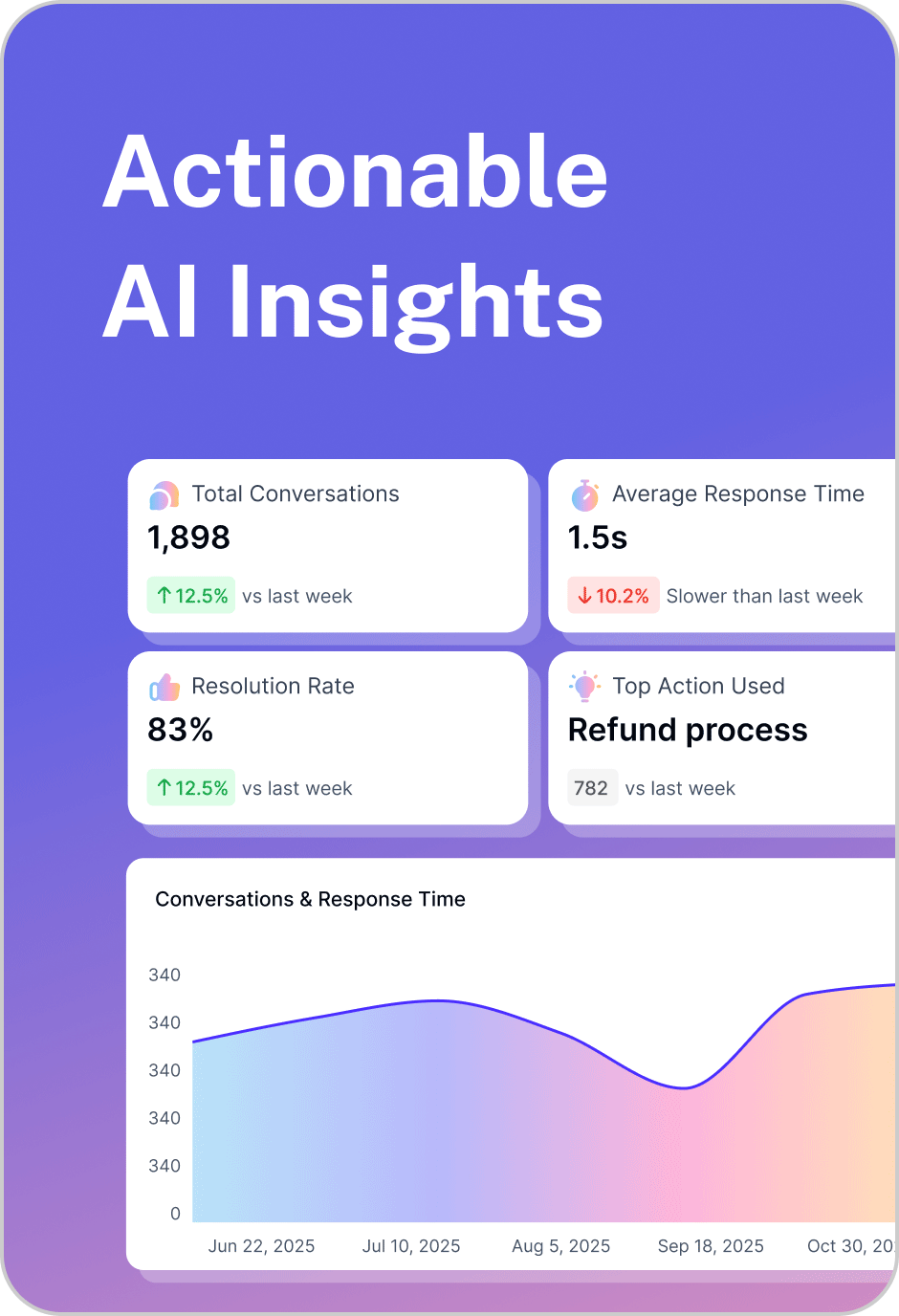
Once validated, deploy the agent across web, Slack, Teams, or WhatsApp. Use built-in analytics dashboards to track engagement, resolution rate, sentiment, and deflection metrics. Iterate continuously with user feedback and analytics insights.
Successful AI agent rollouts follow an incremental automation approach — start with one high-impact use case, prove ROI, then scale to other departments.
Challenges and limitations of AI agents
As powerful as they are, AI agents also introduce new challenges that organizations must manage carefully. From accuracy to compliance, understanding these limitations is key to building safe, reliable, and enterprise-ready systems.
Hallucination and context drift
Even advanced agentic AI systems can sometimes generate inaccurate or overconfident responses, known as hallucinations. This occurs when the reasoning chain lacks enough verified context. Techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and human-in-the-loop review help mitigate this risk.
Security and tool access
AI agents connected to CRMs, HR systems, or databases can pose security risks if permissions aren’t properly scoped. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC), audit logging, and API-level restrictions ensures that agents perform actions safely within approved boundaries.
Ethical and governance concerns
Autonomous decision-making introduces challenges in accountability, transparency, and bias. Businesses must enforce AI governance frameworks and maintain documentation to track decisions made by their agents — especially in regulated industries.
Compliance and data privacy
Enterprises deploying AI agents must comply with frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA. Agents should avoid storing or exposing personally identifiable information (PII) and adhere to region-specific data residency requirements.
Lack of human oversight
Fully autonomous workflows can sometimes act without adequate review, increasing operational risk. Establishing human fallback and escalation paths ensures that sensitive actions — such as refunds or approvals — receive the right level of supervision.
AI governance isn’t just about safety — it’s about trust. Companies that combine autonomy with accountability are more likely to achieve long-term success with their AI agent strategies.
Future trends in AI agents
The evolution of AI agents is accelerating fast. What began as task-specific automation is now expanding into multi-agent ecosystems capable of self-coordination, continuous learning, and complex decision-making. Here’s what the next generation of agentic AI will look like.
Rise of multi-agent collaboration
AI agents are shifting from isolated performers to collaborative systems where multiple agents share information and coordinate tasks. In enterprise settings, planner, executor, and verifier agents work together — much like cross-functional teams — to complete goals efficiently and accurately.
The Agentic Web
Gartner predicts that by 2030, the internet will host an “Agentic Web” — where autonomous agents interact, transact, and make decisions on behalf of users and businesses. These agents will manage everything from scheduling and procurement to personalized content delivery.
Self-improving reasoning systems
Next-gen AI agents will leverage feedback loops, reinforcement learning, and analytics to automatically refine their reasoning abilities. They’ll track past performance, measure outcomes, and adjust workflows without human input — evolving into continuously learning systems.
Hybrid reasoning with RAG and tool-calling
Future agents will blend Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with tool-calling capabilities, enabling them to combine factual retrieval with real-time execution. This hybrid approach ensures higher accuracy and faster responses, especially in mission-critical workflows.
Industry-specific agent marketplaces
Expect to see agent marketplaces emerge, offering pre-built AI agents for finance, HR, IT, or customer support. These plug-and-play models will allow companies to deploy domain-specific agents instantly, reducing development overhead and accelerating ROI.
According to McKinsey, organizations that adopt agentic AI systems early can outperform peers in automation efficiency by up to 40% — marking a major shift from reactive automation to proactive intelligence.
The future of AI isn’t just generative — it’s agentic. Businesses that invest in multi-agent orchestration, governance, and safe autonomy today will lead the transformation of tomorrow’s digital ecosystems.
Build your AI agent today with pagergpt
Whether you're looking to automate customer support, capture more leads, or schedule more meetings, AI agents can take care of the repetitive work so your team can focus on what really matters.
With pagergpt, you don’t need technical skills or complex setups. You can build AI agents that plug right into your workflows from answering customer questions and qualifying leads to booking meetings and handling internal requests.
Here’s what pagergpt offers:
An intuitive, no-code builder to create custom AI agents
Easy training using your website content, help docs, FAQs, or any internal knowledge base
Seamless integration with your existing tools so agents can perform actions without friction
Built-in lead capture capabilities to engage visitors in real time and send qualified leads straight to your CRM
A shared live inbox that helps your team view, manage, and collaborate on customer conversations across channels.
Ready to see what AI agents can do for your business? Start building with pagergpt today
FAQs
Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
No, ChatGPT is not an AI agent. ChatGPT is a powerful language model that can hold conversations, but it doesn’t take actions on its own. An AI agent, on the other hand, is built to perform tasks, make decisions, and interact with other systems based on specific goals.
What is a real-world example of an AI agent?
In e-commerce, a customer support AI agent can answer questions about orders, process return requests, assign tickets to the right team, and schedule follow-ups. It works within support tools like CRMs or helpdesk software to complete these tasks automatically.
What are the types of AI agents?
AI agents come in different types: simple reflex agents, model-based, goal-based, utility-based, learning agents, hierarchical agents, and multi-agent systems. Each type has a different level of intelligence, from a rule-based approach to adapting and making decisions over time.
What are the benefits of AI agents for enterprises?
AI agents help enterprises automate repetitive tasks, reduce response time, improve accuracy, and scale operations. They increase productivity, reduce operational costs, and allow teams to focus on higher-value work while delivering faster, more consistent experiences to users or customers.
What is the difference between ChatGPT and AI agents?
ChatGPT generates responses based on prompts, but it doesn’t take actions or manage workflows. AI agents are autonomous entities designed to achieve goals, trigger workflows, interact with tools, and continuously improve based on feedback and data.
Engage website visitors instantly,
resolve customer queries faster.
Do more than bots with pagergpt
About the Author

Content Writer
Narayani is a content marketer and storyteller with a focus on digital transformation in the B2B SaaS space. She writes about enhancing employee and customer experiences through technology. A lifelong learner, she enjoys reading, crocheting, and volunteering in her free time.